Options trading offers a plethora of strategies with varying levels of risk and reward. One such strategy, the short call option, is an intriguing approach that can yield profits in specific market conditions. But with potentially unlimited risk exposure, how can traders navigate this powerful strategy successfully? This comprehensive guide will dive into the nuts and bolts of short call options, providing you with the knowledge and tools to assess the profit and risk potential effectively.
Key Takeaways
Short call options are a trading technique where an option contract is sold with the expectation that the underlying asset’s price will decrease or remain unchanged.
Risk management techniques such as vertical spreads and rolling short calls can help reduce potential losses when trading short call options.
Practical examples of how various factors affect profitability, along with advanced strategies like vertical spreads and rolling short calls, provide traders increased flexibility to maximize profits while controlling risk exposure.
The Basics of Short Call Options
short call strategy
A short call option refers to an options strategy where a call option contract is sold with the expectation that the price of the underlying asset will either decrease or stay the same. The seller, or writer, of the short call option receives a premium paid by the option buyer. As the writer, you are obligated to sell the underlying asset at the strike price if the option buyer exercises the option.
The short call strategy tends to be most effective when:
The underlying asset’s market price stays lower than the strike price by the expiration date
If the stock trades at a lower price, the option expires worthless, and the writer retains the entire premium collected
However, if the stock’s price rises above the strike price, the writer may face significant losses due to their obligation to sell the underlying asset at a lower price than the current market price.
Related Article: The Ultimate Guide To Mastering The Wheel Strategy
What is a Short Call?
In a short call option scenario, an investor offloads a call option contract with the hope that the price of the underlying asset will either drop or stay unchanged. Short call options can be in-the-money, at-the-money, or out-of-the-money, with the strike price tailored to the trader’s risk appetite and expectations. The probability of earning a profit from a short call option is approximately two-thirds if the price of the underlying asset remains stable or decreases.
For example, consider a situation where a stock is trading at $50 per share, and an investor anticipates a price correction. The investor decides to write a call option with a strike price of $55 and a premium of $2 per share, based on their analysis of the stock’s price. The lot size is 100 shares, yielding an upfront premium of $200 from writing the option.
How Does It Work?
Utilizing a short call strategy involves:
Selling a call option contract, which obligates the seller to provide the underlying asset if the buyer exercises the option.
Submitting a sell-to-open (STO) order to the broker to enter a short call position. This is used to benefit from declining asset prices.
Using a market order to fill the STO order at the asking price.
Using a limit order to fill the STO order at the minimum price an investor is willing to receive.
Time decay, which refers to the decrease in an option’s value due to time passage, is advantageous to short call option sellers. As time passes and expiration approaches, the option’s value diminishes, increasing the profit potential for the writer of the short call option.
However, the risk associated with short call options increases if the stock price exceeds the strike price, as the long call holder may exercise the option, requiring the short call holder to acquire the stock at the prevailing market price, potentially higher than the strike price.
Related Article: Sell To Open Vs Sell To Close
Analyzing Market Conditions for Short Calls
The efficacy of a short call strategy hinges predominantly on market conditions and the trader’s forecast for the price movement of the underlying asset. In bearish or sideways markets, a short call strategy can be advantageous, while higher implied volatility may lead to losses for the option seller.
Understanding the market’s direction and the role of implied volatility is key to determining the most appropriate short call strategy to employ. This section will explore how bearish or sideways markets and implied volatility can impact the performance of short call options.
Bearish or Sideways Market
Bearish or sideways market conditions, where the price of the underlying asset is projected to drop or hold steady, are most suitable for short call options. In a bearish market, a short call strategy can be advantageous as the underlying stock price decreases, thus reducing the value of the short call option and allowing the option writer to retain the premium received. In a sideways market, the option writer may not see considerable changes in the value of the short call option, thus limiting potential gains.
To predict if a market will become bearish or sideways, it is necessary to analyze the price action and observe if prices are consistently closing lower or remaining in a horizontal range. Furthermore, indicators and patterns can be utilized to identify bearish or sideways market conditions.
Importance of Implied Volatility
Implied volatility is pivotal in short call options: increased volatility escalates option premiums, whereas decreasing volatility is advantageous to the option seller. Implied volatility is an indicator of the market’s expectations for future price movements, and when it is elevated, it implies a greater probability of significant price fluctuations, leading to higher option premiums.
Traders can capitalize on implied volatility when engaging in short call options by selling options with high implied volatility, as this allows them to collect more premium upfront. If the underlying stock price remains below the strike price of the short call option, this can result in higher profits. However, a decrease in implied volatility can lead to a decrease in option prices, which may reduce the profitability of the trade.
Related Article: Unlocking The Power Of Extrinsic Value
Profiting from Short Call Options
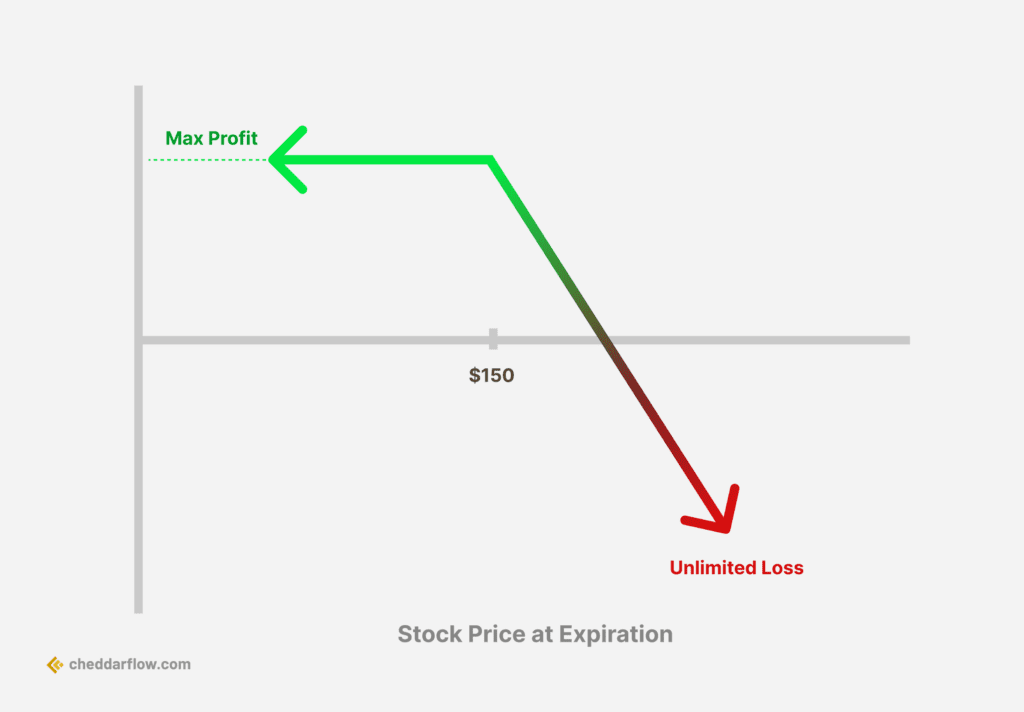
The potential for profit in short call options, which grant the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy the underlying asset at the strike price, is significantly influenced by the erosion of time and implied volatility. The maximum profit achievable from a short call option equals the premium secured from selling the option, whereas the maximum loss is unbounded.
This section will explore the maximum profit scenarios and the factors affecting profit potential.
Maximum Profit Scenario
The maximum profit from a short call option is the premium received from selling the option, as the option seller aims to keep the entire premium if the option expires worthless. The maximum potential loss, however, is unbounded, with the extent of the loss increasing as the underlying asset’s price rises. It is important to note that the short call option strategy carries potentially unlimited risk exposure, requiring traders to be cautious and diligent in their approach.
For example, if an investor sells a call option with a strike price of $50 for a premium of $2 per share, the maximum profit potential is $200 (100 shares x $2 per share). However, if the underlying asset’s price rises significantly, the investor could face unlimited losses, as the potential loss increases proportionally with the price of the underlying asset.
Factors Affecting Profit Potential
Factors such as the strike price, time decay, and implied volatility can impact the profit potential of short call options. Here are some key factors to consider:
The strike price influences the profit potential since the option writer hopes to keep the premium as profit if the underlying asset’s price remains below the strike price.
Time decay benefits the option writer, as the value of the option decreases with time, increasing the profit potential.
Implied volatility can also impact the profit potential, as higher volatility generally leads to higher option premiums.
Assessing Risks Associated with Short Call Options
Short call options inherently come with risks, encompassing the potential for infinite risk exposure. It is essential for traders to understand the risks involved and employ risk management techniques to minimize the potential for loss.
This section will delve into the risks associated with short call options and some strategies to manage those risks.
Unlimited Risk Exposure
With the potential loss escalating as the price of the underlying asset ascends, short call options bear infinite risk exposure. Selling a naked call option, which means selling a call option without owning the underlying asset, entails unlimited risk exposure, as there is no risk mitigation if the stock moves against the position.
The broker will maintain a margin against the account to cover potential losses, and the margin amount depends on the broker, the stock’s price, and market volatility. The profit margin can vary depending on market conditions. This means that it can rise or fall as market volatility shifts. As the price of the underlying asset increases, the risk associated with short call options also increases, potentially leading to significant losses for the option seller.
Risk Management Techniques
Techniques for managing risk in short call options include:
Utilizing vertical spreads: offloading a call option while concurrently purchasing another call option with a higher strike price, which reduces risk exposure and establishes a maximum loss.
Rolling short calls: closing the existing short call position and opening a new short call position with a later expiration date, which can potentially increase profit potential and extend the trade’s lifespan.
Adopting hedging strategies: implementing strategies such as buying protective puts or using other options to offset potential losses.
These techniques can help mitigate risk and improve the overall performance of short call options.
Practical Examples of Short Call Options
To illustrate the profit and loss potential of short call options, let’s examine a few practical examples. These examples will showcase how various factors, such as strike price, time decay, and implied volatility, can impact the profit potential of short call options in different market conditions.
Suppose an investor sells a call option with a strike price of $40 and receives a premium of $3 per share. If the stock price remains below $40 at expiration, the investor keeps the entire premium of $300 (100 shares x $3 per share) as profit. However, if the stock price rises to $45 at expiration, the investor will face a loss of $200 (($45 – $40) x 100 shares – $300 premium). This example demonstrates the importance of carefully selecting strike prices and expiration dates to maximize profit potential and manage risk in short call options.
Advanced Short Call Strategies
Advanced techniques such as vertical spreads and rolling short calls can be beneficial for traders looking to augment their short call options strategies. These advanced strategies offer increased flexibility and risk management opportunities, allowing traders to better navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by short call options.
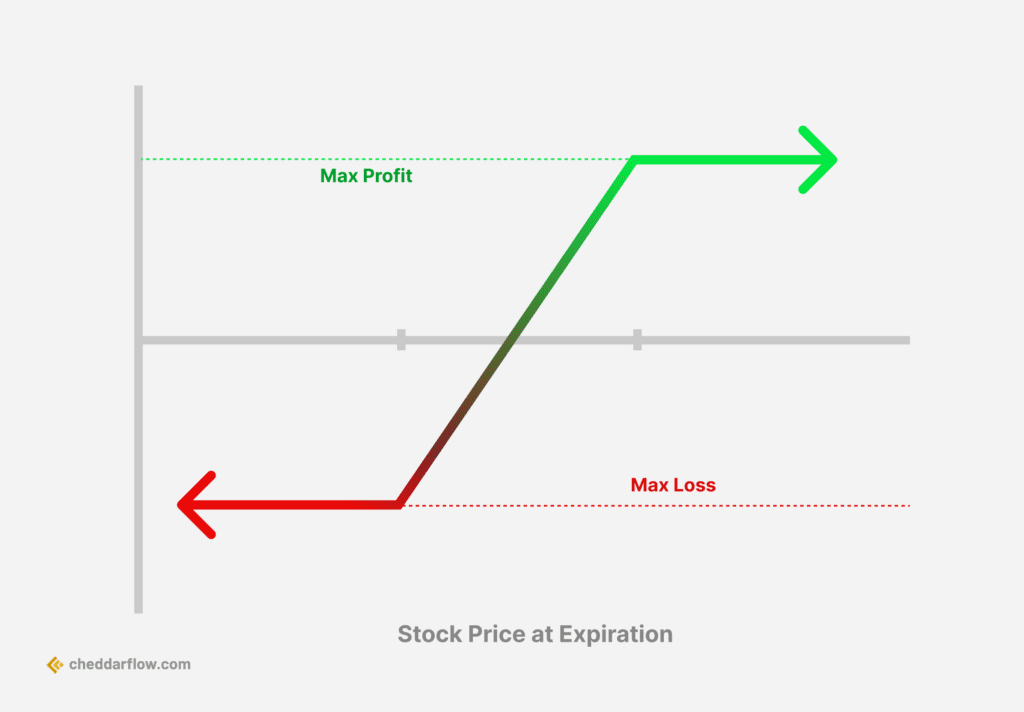
Vertical Spreads
Vertical Spread Strategy
Vertical spreads entail offloading a call option while concurrently purchasing another call option with a loftier strike price, which diminishes risk exposure and establishes a maximum loss. This strategy limits potential losses, as the higher strike call option acts as a hedge against the short call option. If the price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price of the short call option, the loss is offset by the gain in the long call option, thus mitigating the risk of unlimited losses that can occur with a naked short call option.
By carefully selecting strike prices and expiration dates, traders can maximize the potential profit and manage risk effectively when employing vertical spreads in short call options.
Rolling Short Calls
Rolling short calls necessitate wrapping up the existing short call position and initiating a fresh short call position with a postponed expiration date, which could potentially boost profit potential and prolong the trade’s lifespan. Rolling short calls can help traders secure profits, alter strike prices, prolong the time horizon, and control risk.
However, rolling short calls also carries the risk of opportunity cost, as traders may miss out on profits if the underlying security rallies. Furthermore, there may be constraints due to available capital and the risk of the market moving counter to the position. Despite these potential risks, rolling short calls can be an effective advanced strategy for managing short call options.
Summary
Short call options can be a powerful and versatile strategy for options traders who understand the market conditions and risks involved. By carefully selecting strike prices, expiration dates, and employing risk management techniques such as vertical spreads and rolling short calls, traders can navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by short call options with confidence. Remember, while the profit potential of short call options may be enticing, it is essential to remain vigilant and diligent in your approach to managing risk and maximizing opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean to short a call option?
Shorting a call option is a bearish strategy in which an investor sells a call option, expecting the underlying stock to decrease in price. The maximum profit potential of this strategy is limited and the potential risk is unlimited. The trader selling the option is obligated to sell the underlying security at the pre-specified price by the expiry date.
What is long call and short call option?
A long call is a bullish strategy with limited risk that profits when the underlying asset increases in value. On the other hand, a short call is a bearish/neutral strategy with unlimited risk and profits from time decay when the market is neutral or bearish.
What happens when a short call is assigned?
When a short call is assigned, the seller of the option must deliver stock at the strike price and in return receive cash. This results in selling the underlying stock at the strike price and creating a short stock position if there is no offsetting long stock position.
What is the maximum profit potential of a short call option?
The maximum profit potential of a short call option is the premium received from selling the option, providing investors with a fixed return regardless of market conditions.
What market conditions are best suited for short call options?
Short call options are ideal for bearish or sideways markets where the price of the underlying asset is likely to decrease or stay stable.




