What Is A Put Option?
A put option provides the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at the specified strike price by the expiration date. Put options represent a bearish bet on the underlying stock price. Since each put option represents 100 shares of the underlying stock price, a put option is a leveraged position.
Changes in the stock price are magnified by swings in the value of the put option contract. A decrease in the underlying stock price results in an increase of the put option contract. At any point before the contract expiry date, the buyer of the put option can decide to sell the option for a profit or exercise the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
How Do Put Options work?
A put option has two sides to the trade; the buyer and the seller.
The buyer of a put option pays the option premium for the right to sell 100 shares of the stock at the strike price by the expiration date. The buyer will purchase a put option if they are bearish on the stock and believe that it will go down in value within the date of the option contract.
In order for the buyer of the put option to profit, the underlying stock price needs to decrease within the specified time period of the option contract. If the underlying stock decreases in value, the buyer of the contract can either sell the option contract for a gain or exercise the contract in order to sell their shares.
Initially, the buyer is at a loss since they pay the premium. But as the underlying stock price decreases, the value of the options contract increases. As the stock price decreases, the buyer reaches the break-even point where further decreases in the stock price are profitable for the buyer of the option contract.
The seller of a put option earns the option premium in exchange for the obligation to buy 100 shares at the specified strike price if the option buyer decides to execute the contract. Most brokerages require the seller to have the purchasing power of 100 shares of the underlying stock for each option contract bought since they agree to buy the shares if the buyer decides to exercise the contract. By selling a put option, the seller is accepting a capped upside in the form of the option premium.
Different Put Option Strategies Explained
Long put (bearish) – a long put is a bearish bet that the buyer of a put option is making. They are paying the premium of the options contract in hopes of seeing the underlying stock price decrease by the expiry date.
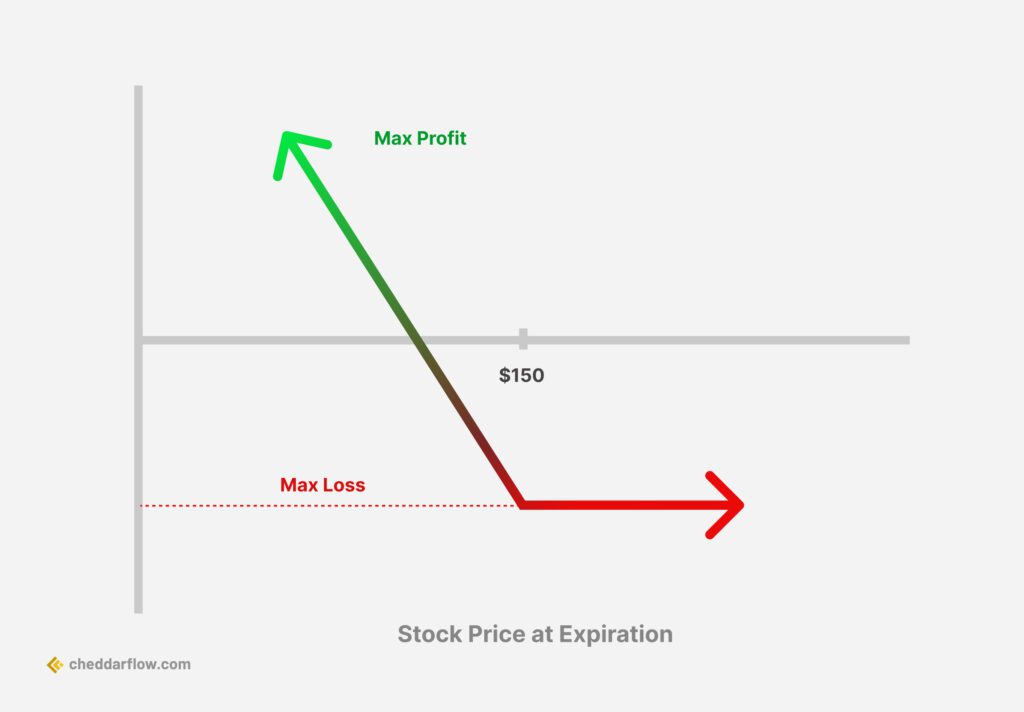
In the above chart, we saw that the buyer pays the premium upfront when buying the put option. If the underlying stock price decreases below a threshold, the buyer will break-even. If the underlying stock decreases beyond the break-even point, the buyer can decide to sell the option contract for a gain.
At any point the buyer can also exercise the option contract in order to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at a premium to the market rate. However, it’s more common to sell the option contract for a gain or let it expire worthless if the break-even price is not reached.
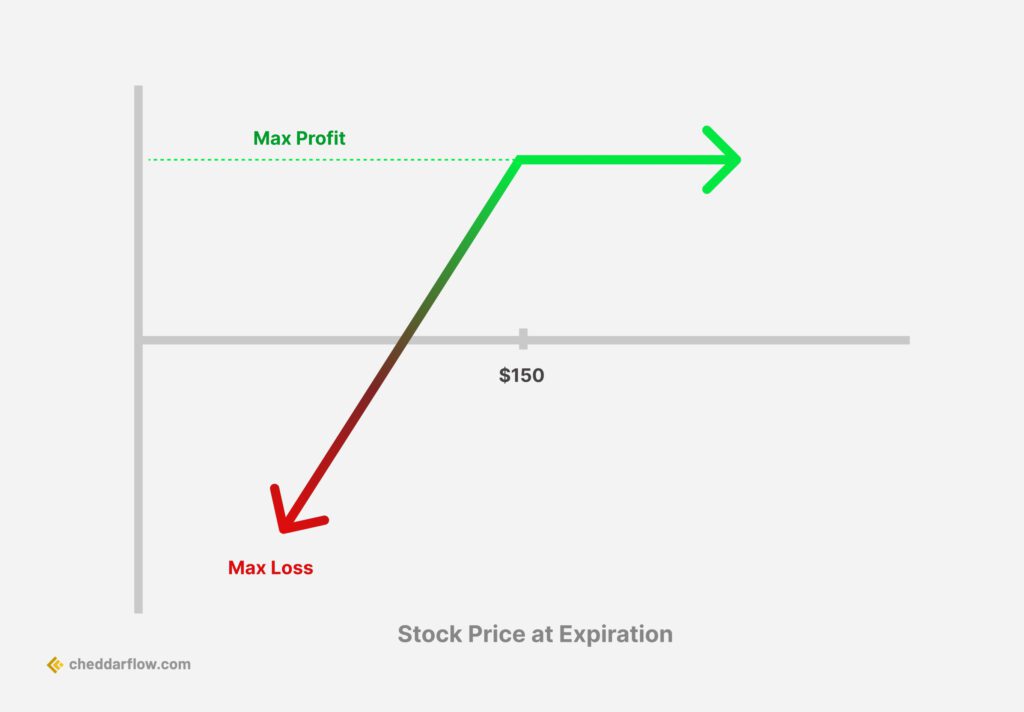
Short put (bullish) – a short call is the position taken by the seller of the put option. They are making a bullish bet that the underlying stock price will stay the same or increase in value by the expiration date. This way they will keep the option premium without needing to purchase the underlying shares at a higher strike price. A short put is sometimes called a “naked put” or an “uncovered put”.
The below chart indicates the profit and loss for a long put and a short put. As demonstrated, the premium of the option contract is initially the loss of the buyer but the profit for the seller. As the underlying stock price decreases in value, the value of the long put bet increases while the value of the short put decreases.
Protective put – a protective put is a strategy involving holding your shares while buying put options to hedge a decrease in the stock price. For example, if you hold 500 shares of a stock, you can also buy 5 put option contracts to hedge your position. If the stock price drastically decreases then you can exercise your put option contract by selling all your shares at the specified strike price and limiting your losses. If the underlying stock price stays the same or increases, you only lose the premium paid for the put options.
Writing Put Options
Writing a put option refers to a trader selling put options. As the “writer” or seller of the put option, you are betting that the underlying stock price will remain constant or increase. As the seller, you collect the option premium for taking the risk of buying 100 shares of the underlying price at the specified strike price within the contract expiry date.
Writing put options is a form of generating income without holding the underlying stock price. Most brokerages require that the seller has the purchasing power of 100 shares of the underlying stock price in order to sell a put option. These funds are used to purchase the underlying shares if the buyer decides to execute the contract.
Benefits of Buying Put Options
Put options allow traders to make a leveraged bearish bet on the underlying stock price. Purchasing a put option provides the option to sell shares at the strike price if the stock goes down.
Put options are also used as a method to hedge your investment. If an investor owns a large number of shares, they may purchase put options to hedge a decrease in the underlying stock price. If the stock goes down, the loss in the stock price is offset by the gain in the options contract. If the stock remains constant or increases, they simply lose the premium.
In addition, put options can be used to generate income.This is done by selling put options and collecting the option premium. To sell a put option you need to have the purchasing power to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock price if the buyer decides to execute the contract.
Conclusion
This article explained put options, a common and complex option contract. To recap:
- A put option offers the buyer the right, but not the obligation to sell the underlying stock at the specified strike price by a certain date
- The buyer of the put option is making a bearish bet on the underlying stock price
- Put options can be used to hedge your position or to generate income by selling put options