Looking to sell options? Want to do it the smart way? In this guide, we’ll be talking about:
- The 10 best options selling strategies
- Pros, Cons, Potential Costs
Now, let’s look at the strategies.
1. Covered Calls
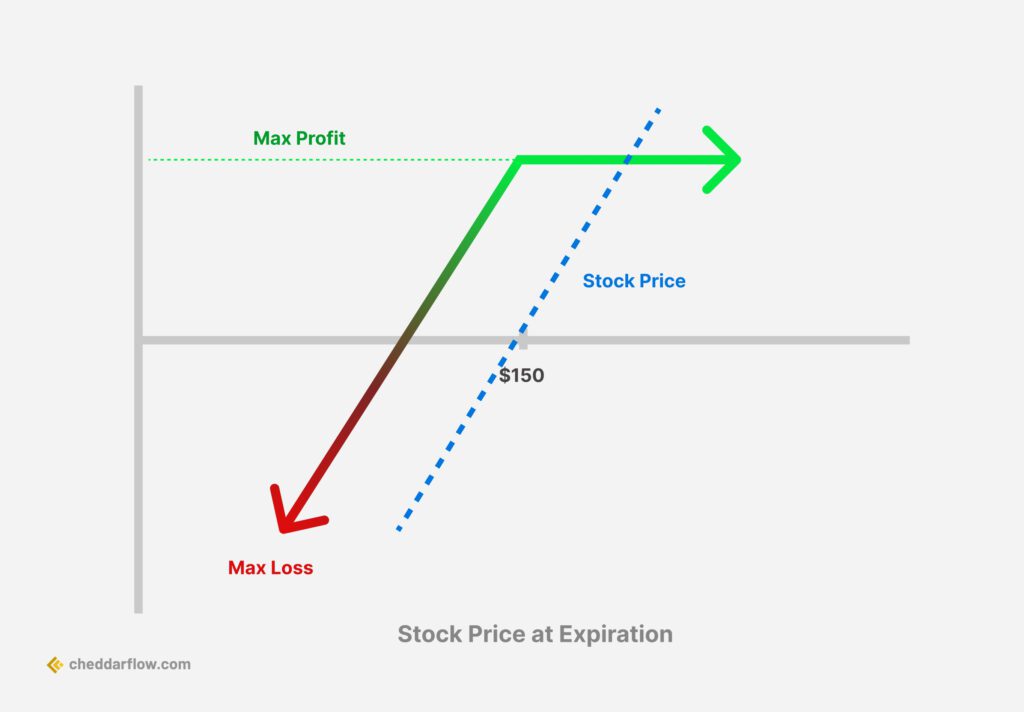
Covered Call Options Strategy
A covered call is an options trading strategy where an investor who owns a stock (or other security) sells a call option on that same asset. This strategy is typically used when the investor has a neutral to bullish outlook on the stock and wants to generate income from it. By selling the call option, the investor collects a premium, which provides some downside protection and can offset a portion of the stock’s potential price drop.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Limited profit potential | A potential loss equal to the difference between the strike price and the price of the underlying asset at expiration |
| Income generation | Underlying asset price could rise above the strike price | The premium received for selling the call option |
| Potential for profit |
Related Article: Sell To Open Vs Sell To Close
2. Naked Puts
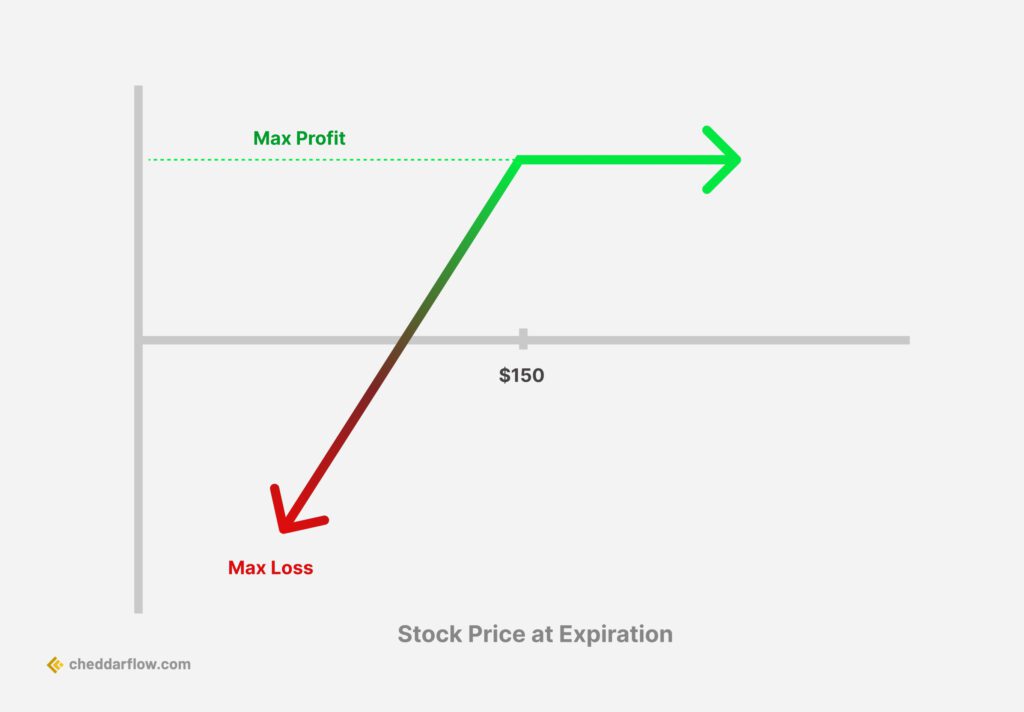
Naked Put Options Strategy
A naked put is an options strategy where an investor sells a put option without holding a short position in the underlying security. The investor profits from the price of the underlying security staying above the strike price of the put option before expiration. This strategy is used when the investor is bullish on the underlying asset and wants to generate income from the option’s premium.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Potential for unlimited profit | Unlimited risk | A potential loss equal to the difference between the strike price and zero, if the underlying asset price falls to zero |
| Higher premium than covered calls | Options seller is responsible for delivering the underlying asset if the option is exercised | The premium received for selling the put option |
Related Article: Master The Short Put Strategy
3. Calendar Spread
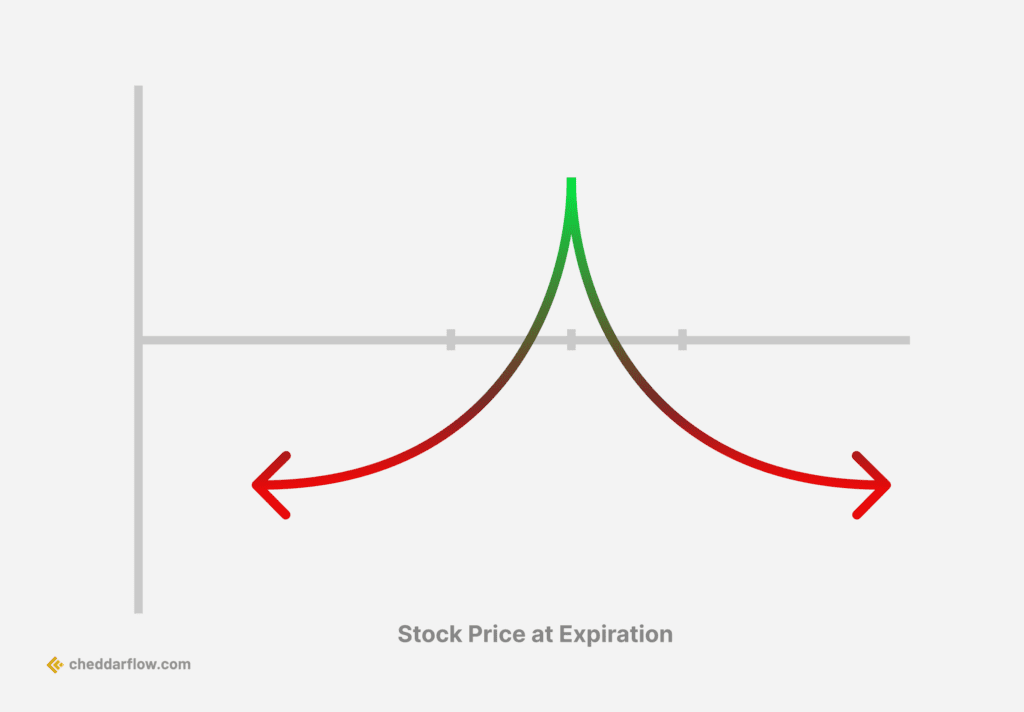
Calendar Spread Options Strategy
A calendar spread is an options strategy that involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but with different expiration dates. It is a market-neutral strategy that aims to profit from the passage of time and/or an increase in implied volatility. The goal is to take advantage of expected differences in volatility while minimizing the impact of movements in the underlying security.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Limited profit potential | The difference between the strike prices, minus the premium received |
| Potential for profit | Exposed to the risk of the underlying asset price moving outside of the specified range |
4. Straddle
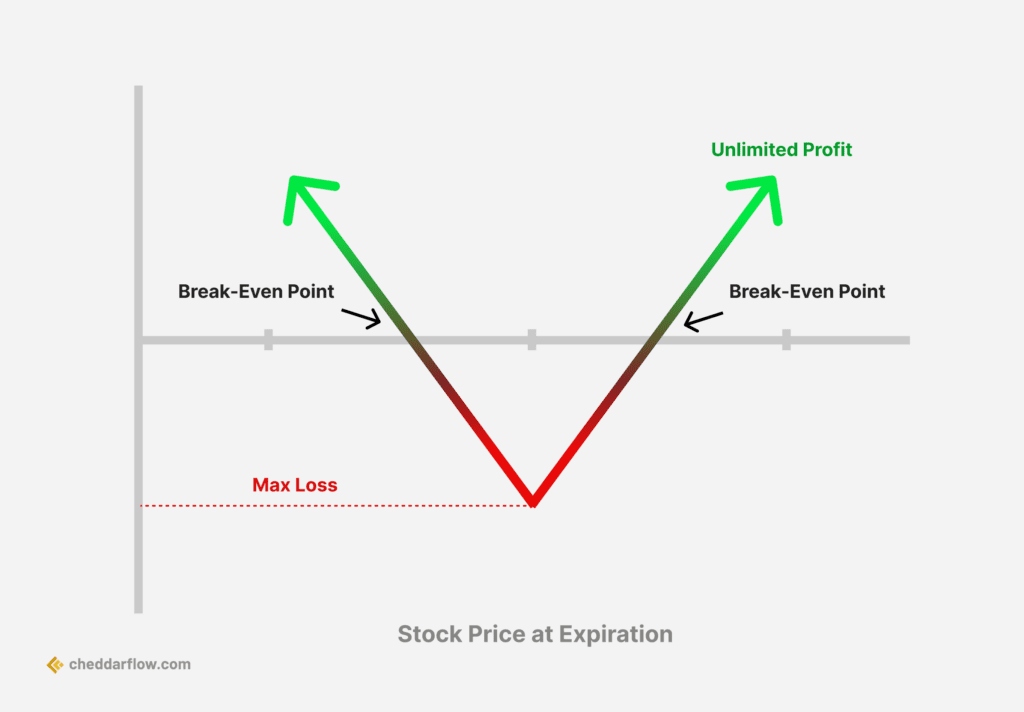
Straddle Options Strategy
A straddle is a neutral options strategy that involves simultaneously buying or selling both a put option and a call option for the same underlying security, with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is used when the investor expects a significant price movement in the underlying asset but is unsure of the direction. A long straddle profits from a substantial price change in the underlying stock, while a short straddle profits from the stock price remaining relatively stable.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Potential for unlimited profit | Exposed to the risk of the underlying asset price moving sideways | The premium received |
| Not required to own the underlying asset | Requires substantial price movement to become profitable | The cost of purchasing the underlying asset if the options are exercised |
5. Butterfly
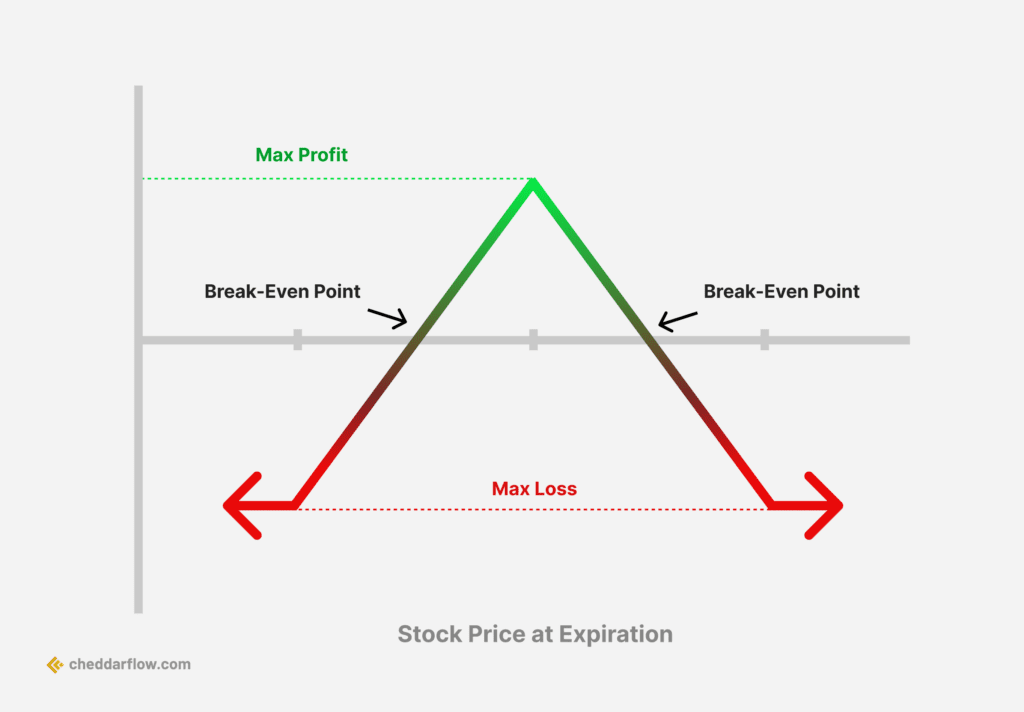
Butterfly Options Strategy
The butterfly options strategy involves the use of four option contracts with the same expiration date but three different strike prices. It is a limited-risk strategy that can be used by traders who believe that the price of an underlying asset will remain relatively stable within a certain range. The strategy consists of buying the wings (an out-of-the-money call or put and an out-of-the-money call or put) and selling the body (two at-the-money calls or puts).
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Limited profit potential | The difference between the strike prices, minus the premium received |
| Potential for profit | Exposed to the risk of the underlying asset price moving outside of the specified range |
6. Iron Condor
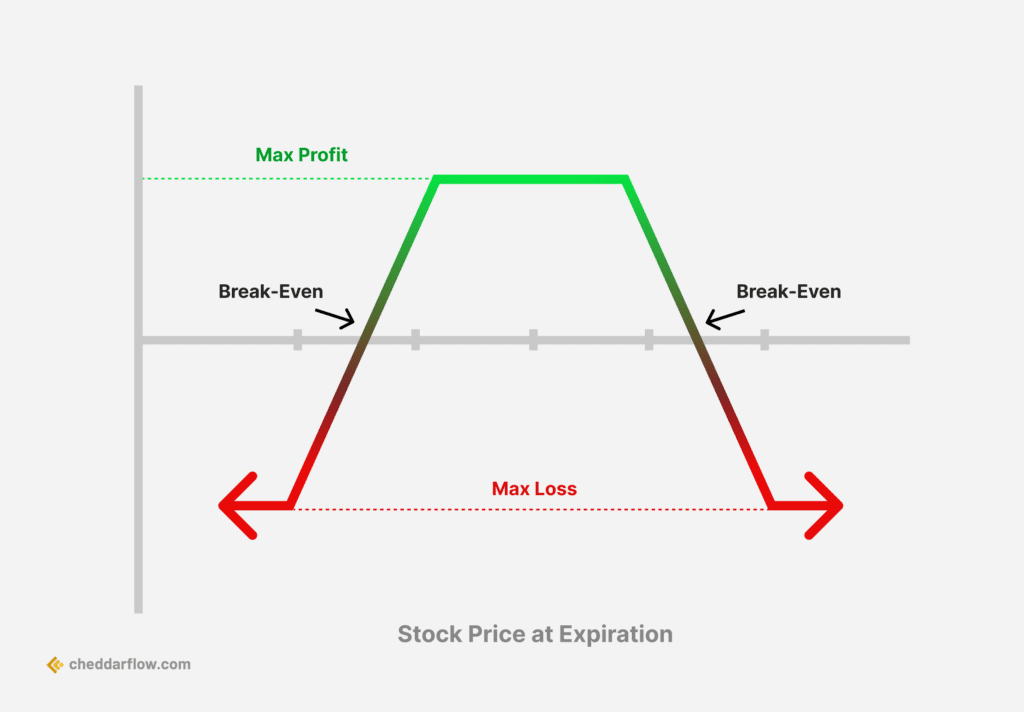
Iron Condor Options Strategy
An iron condor is an options strategy that involves buying and selling calls and puts with different strike prices when a trader expects low volatility. It consists of two puts (one long and one short) and two calls, with four strike prices, all having the same expiration date. The strategy aims to profit from the underlying asset closing between the middle strike prices. It is a market-neutral strategy that benefits from minimal price movement and decreasing implied volatility.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Limited profit potential | The difference between the strike prices, minus the premium received |
| Potential for profit | Exposed to the risk of the underlying asset price moving outside of the specified range |
7. Ratio Spread
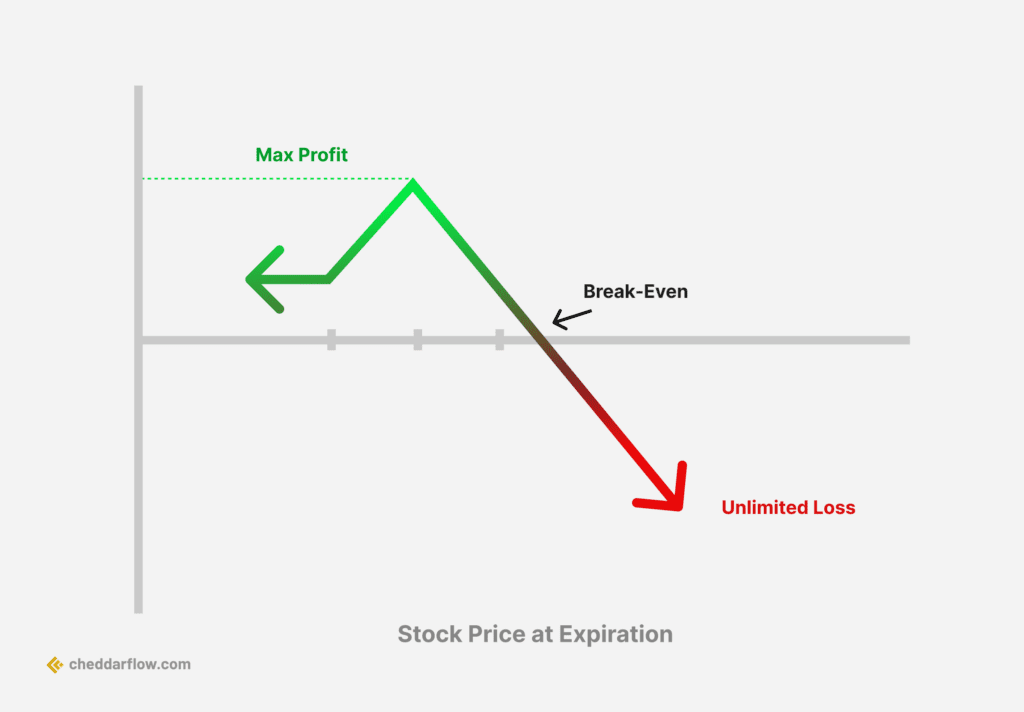
Ratio Spread Options Strategy
The ratio spread is a neutral options strategy that involves buying a number of options and selling more options of the same underlying stock. It is a high-probability trading strategy with a big profit window due to the embedded spread. The most common ratio is two to one, where there are twice as many short positions as long.
Traders use a ratio strategy when they believe the price of the underlying asset won’t move much, although depending on the type of ratio spread trade used, the trader may be slightly bullish or bearish. The setup of this undefined-risk trade is a combination of both long and short options of the same type.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Potential for higher returns | Higher risk | The premium received |
| Potential to generate profits regardless of market direction | Exposed to the risk of the underlying asset price moving outside of the specified range | The cost of purchasing the underlying asset if the options are exercised |
8. Wheel Strategy
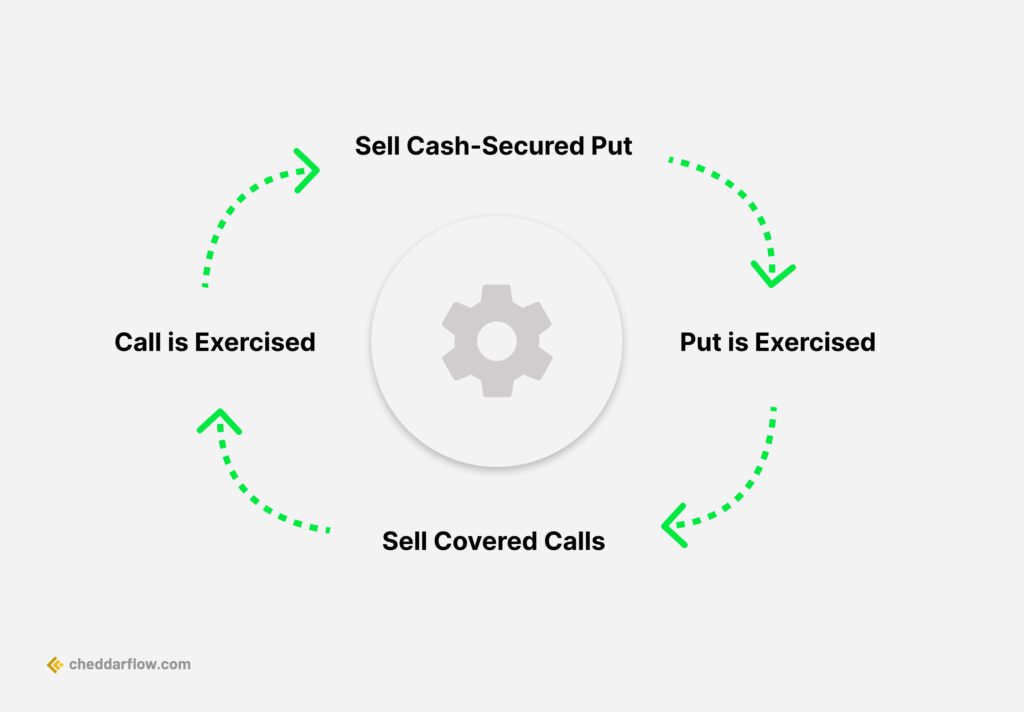
Wheel Options Strategy
The wheel options strategy is a systematic method that combines selling cash-secured puts and covered calls as part of a long-term trading approach. It is designed to generate income by repeatedly selling puts, potentially owning stock, and then selling covered calls until the shares are called away or the position is closed.
The strategy’s primary objective is to consistently take in credit via selling short put options, which can reduce the position’s cost basis throughout its duration. While the strategy offers income-generating potential, it is important to consider that it works best in neutral or slowly trending markets and may not be as effective in highly volatile market conditions.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Requires active management | Cost of buying the underlying asset |
| Potential for income generation | May result in missed opportunities | Premium paid for selling puts |
9. Collar Strategy
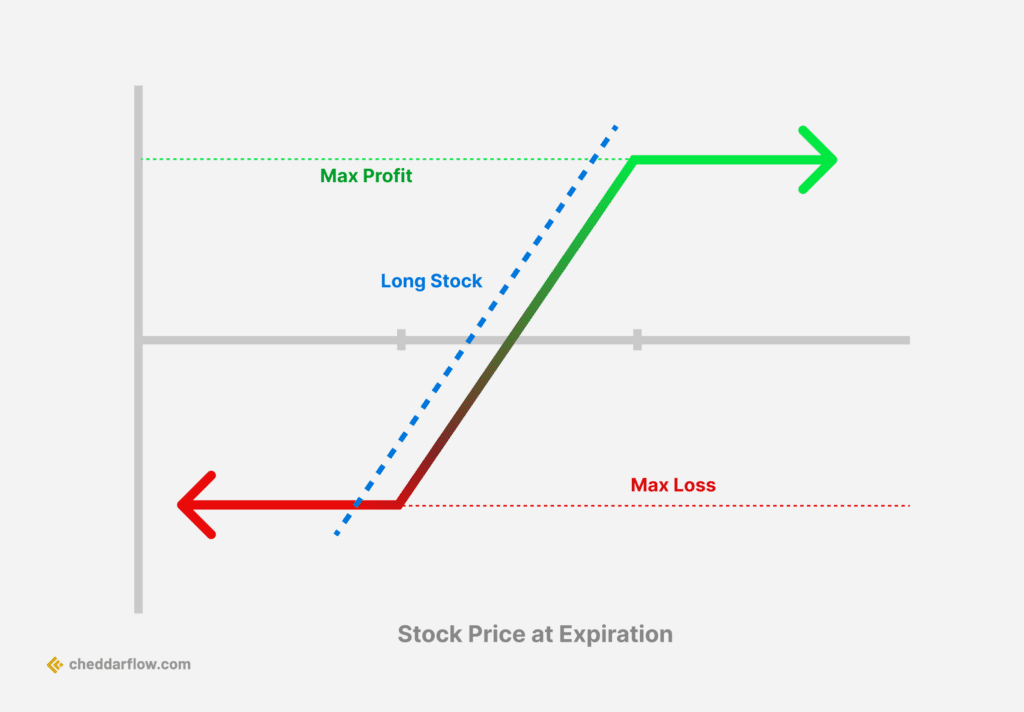
Collar Options Strategy
The collar options strategy is a risk management technique used by investors to protect their portfolios against potential losses while still generating income. It involves buying a protective put option to limit downside risk and selling a covered call option to generate income. This strategy is designed to “collar” the value of an underlying asset within a certain range, thereby reducing the cost of hedging and limiting losses in the event of a market downturn.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Requires active management | Cost of buying a put option |
| Can be used to protect against both upward and downward movements in the underlying asset | May result in missed opportunities | Premium received for selling a call option |
10. Bull Put Spread
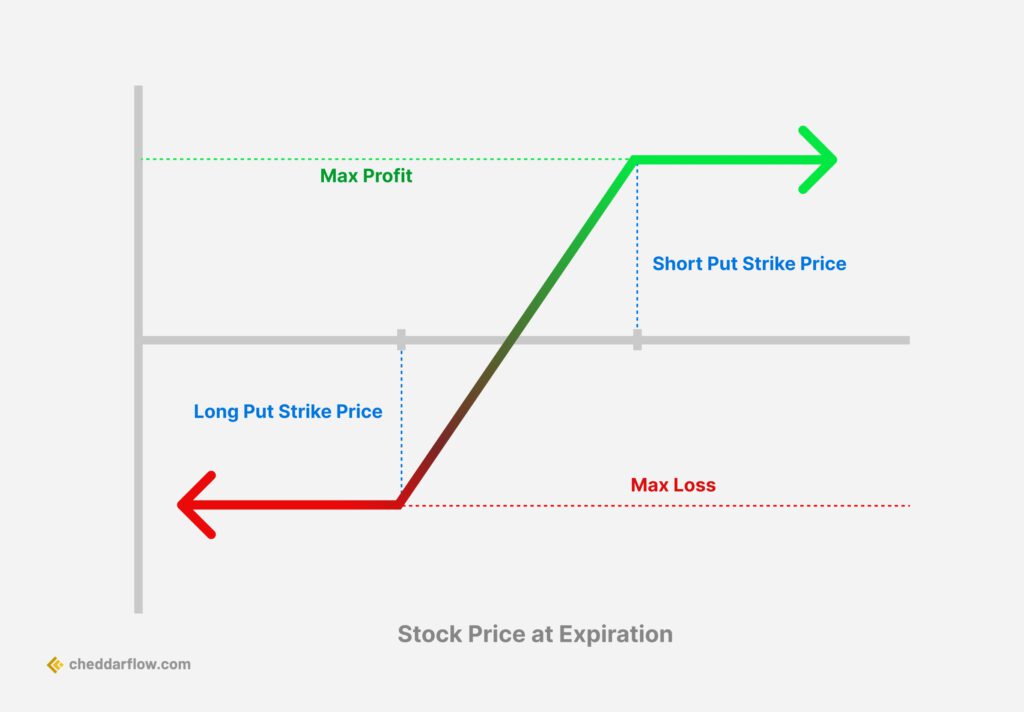
Bull Put Spread Options Strategy
A bull put spread is an options strategy used when an investor expects a moderate rise in the price of the underlying asset. It involves selling a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price. The investor receives a net credit from the difference between the premiums of the two options. This strategy profits from time decay and rising stock prices. The maximum profit is limited to the net premium received, and the potential loss is limited.
| Pros | Cons | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Limited risk | Limited profit potential | The premium received for selling the put option |
| Can be used to hedge against a decline in the underlying asset | Exposed to the risk of the underlying asset price moving significantly above the strike price | The difference between the strike prices |




