Are you seeking a fresh perspective on options trading and looking for a strategy that can generate income while potentially buying stocks at a lower price? Look no further! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the short put strategy, a bullish options trading approach that can help you achieve these goals. Read on to discover the mechanics of short puts, how to analyze risk and reward, and tips for setting up, managing, and adjusting your positions.
Key Takeaways
Short put strategy is an options trading technique that involves selling out-of-the-money puts to generate income and potentially purchase the underlying stock at a reduced price.
Risk/reward analysis must be conducted when considering this approach, as it entails potential for unlimited profit and loss.
Effective management of short put positions can help reduce risk while optimizing profits through techniques such as rolling or converting to spreads.
Understanding the Short Put
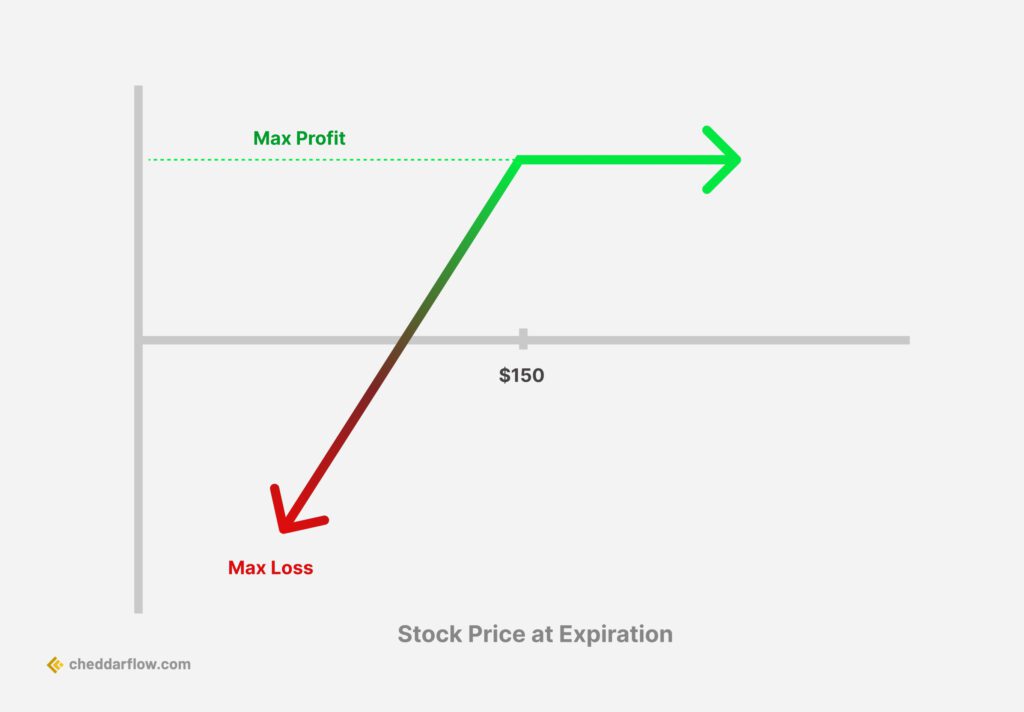
The short put strategy is a popular options trading technique that involves selling an out-of-the-money put option to generate income and potentially purchase the underlying stock at a reduced price. When you sell a put option, you’re contractually obligated to buy the underlying stock at the strike price if the option is exercised, making it a bullish strategy. Short selling options generally, such as this, can be an effective way to generate income and take advantage of market opportunities.
This approach can be attractive to investors who have a positive or neutral outlook on a stock, as it allows them to profit from the premium received when selling the put option and potentially buy the stock at a lower price if the option is exercised. However, one must be mindful of the risks involved. The obligation to buy the stock at the strike price can result in significant losses if the stock price falls.
The basics of selling a put option
When you sell a put option, you receive an immediate premium, which is your maximum profit potential if the stock price stays above the strike price and the option expires worthless. However, if the stock price drops below the strike price, you’ll be obligated to buy the underlying stock at the strike price, potentially incurring losses.
Entering a short put position involves submitting a sell-to-open order to your broker, indicating the desired stock price at which you intend to sell the put option. Maintaining an adequate cash balance in your account is critical to cover potential stock purchases if the option is exercised, considering the higher risk associated with naked options strategies involve. As you navigate the world of stock trades, it’s essential to understand these risks and manage your portfolio accordingly.
Related Article: Mastering The Wheel Strategy For Profitable Options Trading
Bullish strategy for short puts
A short put is considered a bullish strategy because:
The seller benefits from the stock price staying above the strike price, allowing the option to expire worthless and keeping the premium received.
The maximum gain is limited to the premium received from selling the put option.
The risk is potentially significant if the stock price falls below the strike price and the seller is obligated to buy the stock.
For example, if the strike price for the put option is $32.50, and the stock price is above the strike price at expiration, the potential gain is the premium generated from selling the option. However, if the stock price falls below the strike price, the short put seller would be required to purchase the stock at the strike price, exposing them to potential losses.
Analyzing Risk and Reward

In the process of considering a short put strategy, assessing both the potential rewards and the inherent risks is a crucial step. The potential rewards include the premium received from selling the put option and potential profits from a bullish or neutral market outlook. If the underlying stock price stays above the strike price of the put option, the strategy can offer unlimited profit potential.
However, the risks associated with short put strategies can be substantial. The seller may be exposed to considerable risk if the stock price falls below the strike price, as they are obligated to purchase the stock at the strike price. Furthermore, a short put strategy carries an undefined risk exposure due to the potential for unlimited losses.
Limited profit potential
The maximum profit for a short put is limited to the premium obtained from the sale of the option. The strike price of a short put option has a direct correlation to the premium; the closer the strike price is to the current price of the underlying security, the higher the premium will be, and vice versa. This is due to the effect the proximity of the strike price has on the likelihood of the option being exercised, which impacts the perceived risk and value of the option.
The expiration date of a short put option can also have an effect on its premium. Generally, options with later expiration dates tend to have higher premiums due to an increased time value. As the expiration date approaches, the time value of the option decreases, resulting in a lower premium. However, other factors such as the underlying stock price and expected volatility may also influence the price of the put option.
Undefined risk exposure
Short put sellers face significant risk if the stock price falls below the strike price, as they are obligated to buy the stock at the strike price. The break-even price for a short put position is calculated by subtracting the premium collected from the strike price.
The potential loss in this scenario is calculated as the difference between the strike price and the stock price, multiplied by the number of shares, minus the premium received from selling the option. The maximum potential loss in a short put option strategy can be calculated by subtracting the credit received from the strike price.
Setting Up and Executing a Short Put
Setting up a short put strategy requires careful selection of the right strike price and expiration date. Factors to consider include:
The desired income or profit
The anticipated time frame for stock stability or increase
Risk tolerance
Prevailing market conditions
Market volatility, for example, can impact the selection of strike price and expiration date, influencing the premium received and the potential for price movements.
Additionally, the most suitable expiration date for a short put option depends on the trader’s desired timeframe and market outlook. Generally, it is common to select an expiration date that is between 3 weeks and 45 days from the present date, balancing the trade-off between time decay and the potential for assignment.
Selecting the right strike price
When choosing a strike price for a short put option, consider factors such as the desired entry point for the underlying stock, the premium received, and market volatility. If the desired entry point is lower than the current stock price, a lower strike price may be chosen to maximize the potential for profit if the stock price decreases. On the other hand, if the desired entry point is higher than the current stock price, a higher strike price may be selected to maximize the potential for profit if the stock price increases.
The premium received has a direct correlation to the selection of the strike price for a short put. A higher premium received will result in a higher strike price, thus reducing the risk of loss but also the potential profit. Conversely, a lower premium received will result in a lower strike price, thus increasing the potential profit but also the risk of loss.
Determining expiration dates
The expiration date of a short put option can play a crucial role in determining the success of the strategy. Theta, also known as time decay, is advantageous for put option sellers. This is because their options will lose value as the expiration date nears. Therefore, selecting an appropriate expiration date that balances the trade-off between time decay and the potential for assignment is essential.
Typically, options with later expiration dates tend to have higher premiums due to increased time value. As the expiration date approaches, the time value of the option decreases, resulting in a lower premium. However, other factors such as the underlying stock price and expected volatility may also influence the price of the put option.
Related Article: What Is Theta In Options Trading
Managing and Adjusting Short Put Positions
Skillful management and adjustment of short put positions are key in minimizing risk and maximizing profit potential. Techniques such as adjusting the strike price, expiration date, and other options positions can help achieve these goals.
Indications that a short put position requires adjustment include:
The stock price moving against you
Increasing implied volatility
The position moving closer to being in-the-money
Debit adjustment
Employing strategies like rolling and converting to spreads can mitigate these risks and improve your positions.
Rolling strategies
Rolling a short put involves closing the current position and opening a new one with the same strike price but a later expiration date. This strategy allows you to capture more premium, extend the trade’s duration, and potentially increase your profit potential.
However, rolling a short put also carries risks. Some potential risks when rolling a short put strategy include:
Taking a loss on the front-month put
Not securing any gains on the back-month put
Facing the possibility of purchasing the corresponding stock at an unfavorable market price.
Converting to spreads
Converting a short put to a spread involves adjusting the short put position by adding a long put with a lower strike price, thus creating a bull put spread and limiting downside risk. This strategy can limit potential losses while potentially increasing profits by combining the short put with other options positions.
By adding a long put with a lower strike price, you can provide insurance against a decline in the price of the underlying asset, thereby limiting downside risk. This strategy offers several advantages, such as risk management, augmented profit potential, and adaptability.
Dividends and Their Impact on Short Puts
Dividends can have a significant impact on short put strategies. When a stock goes ex-dividend, the stock price usually decreases by the amount of the dividend, which can affect the strike price of a short put option. The strike price may be adjusted downwards to reflect the reduction in the stock price and maintain the option’s value.
An impending dividend payment can also influence the timing of exercising a short put option. Generally, put options become more expensive as the stock price decreases due to the dividend payment. Thus, if a short put option has been written, the value of the option may increase as the dividend payment approaches, making it prudent to consider exercising the short put option before the dividend payment to avoid potential losses.
Hedging Techniques for Short Puts
One effective hedging technique for short put positions is creating a short straddle by selling a call option with the same strike price and expiration date as the short put. This strategy can help reduce risk by generating additional income and extending the break-even price above and below the centered strike price of the short straddle.
However, recognizing the risks associated with a short straddle is important. The risk beyond the premium received remains unlimited should the stock price continue to decrease. Therefore, it’s crucial to employ other risk management techniques, such as rolling strategies and converting to spreads, to further mitigate potential losses.
Synthetic Short Put Strategies
A synthetic short put is a combination of a long stock position and a short call option at the strike price of the original long stock position, resulting in a payoff diagram similar to that of a single short put option. This strategy can help traders replicate the mechanics of a short put without actually selling a put option.
Summary
The short put strategy offers a unique approach to options trading, providing income generation and the potential to buy the underlying stock at a lower price. By understanding the mechanics of short puts, analyzing risk and reward, and effectively managing and adjusting positions, investors can harness the power of this bullish strategy. As with any trading strategy, it’s essential to evaluate the potential risks and rewards, stay informed about market conditions, and adjust positions as needed to succeed in the ever-changing world of options trading.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of a short put?
Selling a put option in anticipation that the price of the underlying stock will remain above a specific level is what a short put entails. For example, if you believe AAPL will remain above $140 in two months, you could sell a put option with a $140 strike price and 60 days to expiration. Alternatively, if you wish to buy a security at a specific price, you could sell a put option with that strike price; should the price fall below the strike, you will be obligated to purchase the security.
What is long put and short put?
A long put is when an investor buys a put option, expecting the underlying asset’s price to decrease, while a short put (also called a naked put) involves selling a set option and obligating the seller to buy the underlying asset at the strike price if assigned.
Is short put bullish or bearish?
The short put is a bullish options trading strategy, used when you expect the price of an underlying security to rise. It has low profit potential and is exposed to unlimited risk, but it’s a good strategy for small price increases.
How much can you lose on a short put?
The potential loss for a short put strategy can be substantial, given that there’s no cap on how far the stock price could drop.
What is short call?
A short call is a bearish options trading strategy where an investor writes (sells) a call option, expecting the underlying asset’s price to fall. This has limited profit potential and carries the risk of unlimited losses.




