Trading in the stock market can be a thrilling ride, filled with opportunities and risks. One of the most intriguing and deceptive phenomena traders may encounter is the bear trap. This deceptive market event can lead to significant losses if not properly understood and navigated. In this blog post, we will dive into the intricacies of bear traps, explain how they operate, and provide strategies to avoid falling prey to them.
Key Takeaways
Bear traps are a situation where investors mistakenly think prices will decrease, only to be trapped when prices unexpectedly rise.
To successfully navigate bear traps, traders must employ risk management techniques and exercise patience.
Real life examples of bear traps can help inform strategies such as shorting and long term opportunities for potential profits.
Understanding Bear Traps
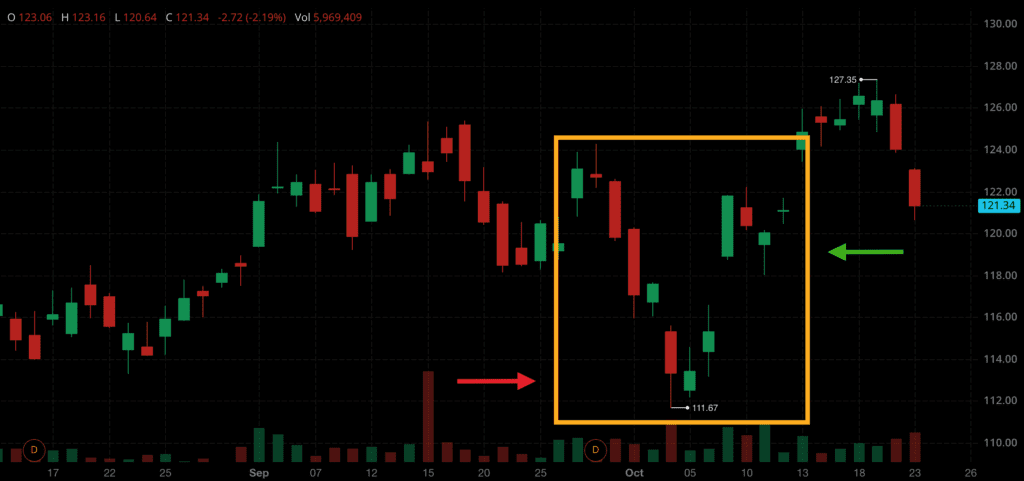
In a bear trap scenario, prices suddenly fall, leading bearish investors to sell short. However, prices unexpectedly rebound, causing losses for those who had sold short. Bear traps may be precipitated by a range of occurrences, such as:
government report releases
geopolitical events
company press releases
rumors of a recession
These events can lead to falling prices, a downward trend, and a lower price, while other factors may cause prices rise.
Technically, a bear trap is defined as a situation where investors mistake a price decrease as an indication of further selling, but end up trapped when prices surge, contrary to their expectations.
The Mechanics of a Bear Trap
A bear trap unfolds when a stock or another asset witnesses a significant price drop, triggering short-selling activity. The subsequent price reversal traps bearish investors who had anticipated further price decline. Short sellers play a crucial role in bear traps as they are obligated to cover their positions as prices elevate to reduce losses. Short-sellers purchase instruments to cover their short positions. This triggers buyers to start buying, causing the asset’s downward momentum to reduce..
Support levels are important in the mechanics of a bear trap. A support level is a level at which bullish investors have previously demonstrated an inclination to purchase stocks, providing support for shares as they tend to rebound off these levels. When markets surpass support levels, technicians advise that additional selling is likely, and traders should pay close attention to price action. A subsequent rise in buying activity, possibly driven by bullish investors, could potentially catalyze additional gains, thereby continuing to propel price momentum.
Price Reversal
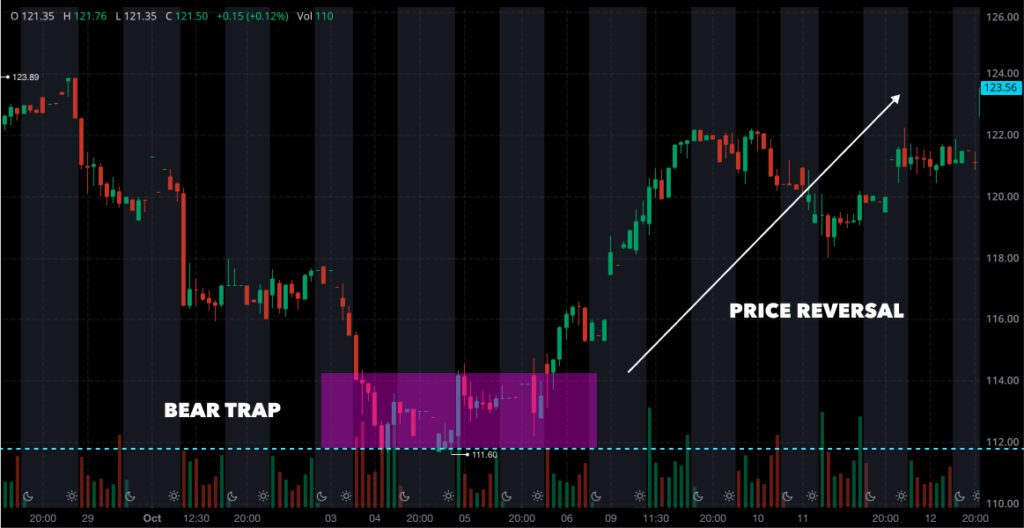
A bear trap price reversal is a situation in trading wherein the price of a stock or asset appears to be transitioning from a bullish trend to a bearish trend, yet then abruptly reverses back to a bullish trend. This trap ensnares bearish traders who may have shorted the stock or asset in response to the initial bearish signals. The cause of bear trap price reversals arises when the market trend shifts direction, leading to losses for traders ensnared in the trap.
Bear trap price reversals may be identified by observing signs of a reversal in the market trend, such as a sudden increase in volume or a sharp change in price. Additionally, technical indicators such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands may be utilized to detect bear trap price reversals.
To avoid falling prey to bear trap price reversals, traders can employ risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders and using proper position sizing. They should also be patient and wait for the right moment to enter or exit a trade.
Identifying Bear Traps in the Market
Recognizing bear traps is a key skill for traders seeking to steer their way through the volatile stock market. Bear traps can be identified by observing sudden price drops, short selling activity, and subsequent price reversals.
In addition to these observations, technical indicators, market trends, and sentiment can be utilized to identify bear traps.
Technical Indicators
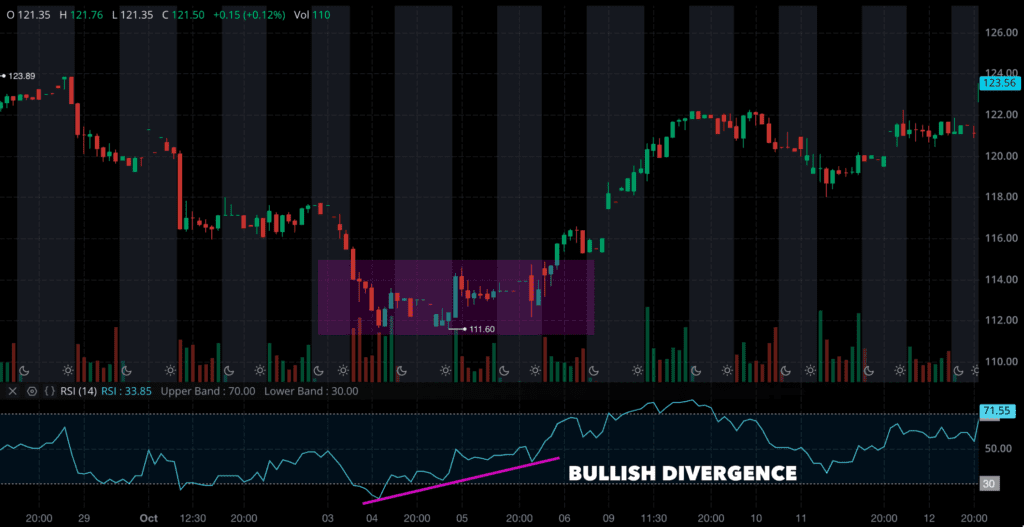
Momentum indicators, such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and the Relative Strength Index (RSI), can aid in distinguishing a true reversal from a bear trap. A divergence, which is when the MACD and RSI values are increasing while the price is decreasing, suggests that the price movement may be a bear trap.
Fibonacci levels can also assist in determining a bear trap. Verifying if a downward price movement is breaching Fibonacci levels in conjunction with support levels can help traders identify potential bear traps.
Other technical indicators that can be employed to identify bear traps include the RSI, moving averages, the currency strength indicator, and volume indicators.
Market Trends and Sentiment
Market trends and sentiment analysis is a technique for examining the market to ascertain potential bear traps. It involves examining the overall market sentiment, in addition to the trends in the market, to determine whether a bear trap is likely to occur.
Examples of market trends and sentiment analysis include examining the overall market sentiment, analyzing the cost movements of a security, and considering technical indicators such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands.
How to Avoid Falling Prey to Bear Traps
To avoid falling prey to bear traps, traders must employ risk management techniques and exercise patience. Stop-loss orders and diversification may be utilized to reduce the likelihood of bear traps.
Additionally, timing and patience are indispensable when it comes to evading bear traps, as traders ought to be mindful of potential reversals and not hasten into short positions.
Related Article: Equity Trading: What It Is, How To Trade
Risk Management Techniques
To sidestep bear traps, traders could implement strategies such as:
Setting stop-loss orders
Diversifying their portfolios
Hedging
Avoiding illiquid markets
Adhering strictly to risk management measures
A stop-loss order is an order placed with a broker to buy or sell a security when it reaches a certain predetermined price, intended to limit an investor’s loss on a security position.
Diversification is a risk management technique that involves investing in a variety of different assets to mitigate the potential for loss from any one asset. Other risk management techniques that can be employed to avoid bear traps include:
Hedging strategies
Avoiding illiquid markets
Implementing a disciplined approach with risk management measures
Using stop-loss orders
Timing and Patience
Timing and patience are essential for circumventing bear traps, as traders ought to be vigilant of potential reversals and not hasten into short positions. By exercising patience and discipline, traders can circumvent bear traps and minimize potential losses.
Some examples of timing and patience techniques to avoid bear traps include remaining composed, adhering to one’s trading plan, and refraining from impulsive decisions.
Comparing Bear Traps and Bull Traps
Traders operating in the stock market need to be vigilant of two major traps – bear and bull traps. A bear trap is a false indication of a reversal from an uptrend into a downtrend, whereas a bull trap is a false indication of a reversal from a downtrend into an uptrend.
Understanding the differences between these traps and the common mistakes made by traders can help navigate the market more effectively.
Key Differences
The primary distinction between bear traps and bull traps is the direction of the false signal and the market position they aim to affect. A bear trap targets sellers or short sellers in an unfavorable trade, while a bull trap targets buyers in an unfavorable trade.
These differences impact the trading strategies used to navigate the market, taking into account trading volume, and protect against potential losses.
Common Mistakes
Common mistakes made by traders when dealing with bear traps and bull traps include misinterpreting market signals and not employing appropriate risk management techniques.
To avoid making these mistakes, traders should approach trading with a prudent and analytical attitude, remaining aware of prevalent errors such as low trading volume, the absence of trend break, the absence of confirmation, unidirectional mentality, and purchasing high and selling low.
Trading Strategies Around Bear Traps
In relation to bear traps, traders can adopt strategies including:
Technical analysis
Execution of stop-loss orders
Diligent risk management
Close monitoring of market indicators
Keeping abreast of market news and developments.
Shorting strategies and long-term opportunities are two specific strategies that can be employed to navigate bear traps.
Related Article: Uncovering The CNN Fear And Greed Index
Shorting Strategies
For shorting strategies, traders can place stop orders and consider taking long positions during downtrends if the fundamentals are strong. Additionally, they may establish a short position when expecting a security’s price to decline. Stop orders are used to buy or sell a security when it reaches a predetermined price, while long positions during downtrends involve purchasing a security when the price is low and disposing of it when the price increases.
By using these strategies, traders can take advantage of market fluctuations and capitalize on potential profits.
Long-Term Opportunities
Bear traps may offer investors the chance to acquire extra shares at reduced prices, which could prove advantageous in the long term. When a bear trap is established, the stock price will diminish, thus providing investors with the possibility to acquire additional shares at a reduced cost.
This may prove to be advantageous in the long term for a bullish investor, as the stock price may eventually recover.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the mechanics of bear traps and employing effective trading strategies can help traders navigate the complex world of stock trading. By utilizing technical indicators, market trends, sentiment analysis, risk management techniques, and patience, traders can minimize potential losses and maximize profits. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed and adapting to new challenges will remain crucial for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a bear trap?
A bear trap is a form of market manipulation in which traders are deceived into believing that the price reversal indicates the start of a downtrend, when instead it is followed by a sharp resumption of the previous uptrend. It occurs when there is a bearish correction or reversal amid an overall uptrend, with shorting temporarily overcoming buying pressure and causing a short-term price fall.
What are some technical indicators that can assist in identifying a bear trap?
Technical indicators such as MACD and RSI can assist in identifying a bear trap by helping to distinguish a true reversal from a false one.
How can I avoid falling prey to bear traps?
To avoid falling prey to bear traps, use risk management techniques, exercise patience, and utilize technical indicators, market trends, and sentiment analysis.




