Have you ever wondered how professional investors uncover hidden gems in the stock market? One answer lies in the concept of “overweight” stocks. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the meaning of overweight stock ratings, the importance of market capitalization, and the benefits of diversifying your investment portfolio with these potentially high-performing stocks. Get ready to gain valuable insights that could transform your approach to investing, and understand “what does overweight stock mean” in the world of finance!
Short Summary
Analysts assign an “overweight” rating to stocks with potential for outperforming their peers or the market.
Investors should take into account analyst ratings, past performance and market capitalization when making investment decisions.
Adding overweight stocks to a diversified portfolio can potentially increase returns while reducing risk.
Decoding Overweight Stock Ratings
When navigating the complex world of investing in stocks, understanding the language of stock analysts is crucial. Among these terms, “overweight” stocks play a significant role in shaping investment decisions. In essence, an overweight stock rating signals that analysts believe a particular stock will outperform its peers or the overall market, making it a potentially attractive investment opportunity.
But what exactly does “overweight” mean, and how can investors make the most of this information? Read on to find out.
Overweight Stock Rating Defined
An overweight stock rating is an analyst’s assessment that various factors, such as favorable news or earnings, are likely to bolster a stock’s performance. This bullish recommendation implies that the stock has the potential to outperform other stocks in the same industry or the market as a whole.
Some factors that may lead analysts to give a stock an overweight recommendation include a consistent flow of positive news, satisfactory earnings, and improved guidance. When assessing a stock for an overweight rating, investors should consider the company’s historical performance, the analyst’s track record, and the company’s market capitalization.
Implications for Investors
An overweight rating suggests that the stock is expected to perform better than the market or benchmark, thus making it a viable option for investors. However, it’s important to remember that an overweight rating is not a guarantee of success.
Investors should consider other factors, such as past performance and market capitalization, alongside the rating to make informed decisions. Additionally, investment time horizons and risk tolerance should be taken into account when interpreting an overweight rating.
Rating Systems: Three-Tier vs. Five-Tier

To better understand the concept of overweight stock ratings, it’s essential to grasp the rating systems used by stock analysts. The two primary rating systems are the three-tier and five-tier systems. The three-tier system usually consists of “buy,” “sell,” and “hold” ratings, while the five-tier system incorporates additional categories such as “outperform” and “underperform”.
In this context, an overweight rating falls between “hold” and “buy”. Let’s dive deeper into these systems and see how they can influence your investment decisions.
Three-Tier System
The three-tier system is a stock rating system employed by analysts that comprises three tiers: Underweight, Overweight, and Equal Weight. In this system, an “overweight” rating can be interpreted as a “buy” recommendation. This means that if a stock is rated as overweight, the analyst believes that the stock will outperform its peers or the market, making it a potentially attractive investment.
Five-Tier System
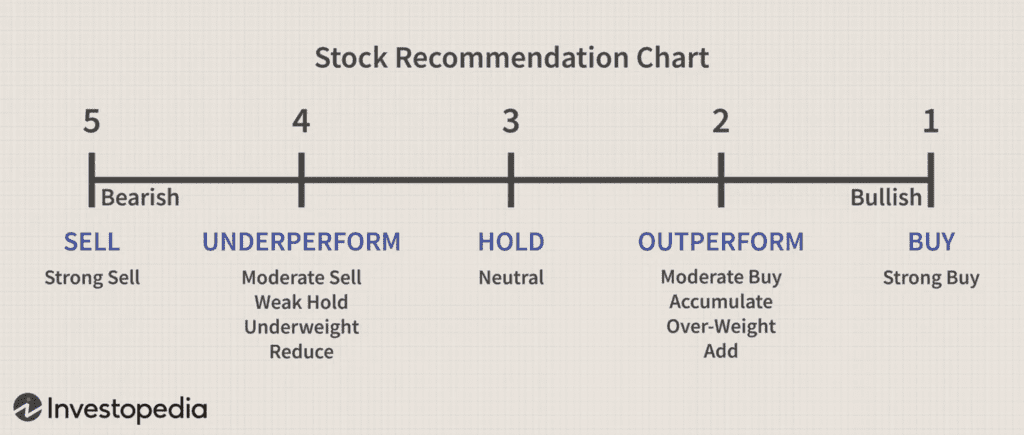
Image from investopedia
On the other hand, the five-tier system in the stock market is a rating system that comprises five levels: buy, overweight, hold, underweight, and sell. This system is utilized by stock analysts to conduct research and issue recommendations.
An overweight stock rating usually falls between Buy and Hold, or occasionally between Strong Buy and Buy. This means that a stock with an overweight rating is expected to outperform its peers or the market, positioning it as an appealing investment opportunity.
The Role of Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is a critical factor in the world of investing, especially when it comes to benchmarking stocks. The Standard and Poor’s 500 index is a popular benchmark to judge the stock market performance. It consists of 500 large companies, which closely reflect the overall market trend.
In the context of overweight stocks, market capitalization can be an essential consideration when determining the weight of a stock in an analyst’s rating. Let’s explore the concept of market capitalization in more detail.
Market Capitalization Defined
Market capitalization, often abbreviated as “market cap,” is the total value of a company’s outstanding shares of stock. It is calculated by multiplying the current market price of one share by the total number of outstanding shares.
Market capitalization is a key indicator of a company’s size and worth, and it plays an important role in investment decisions.
Impact on Investment Portfolio
Market capitalization is a crucial factor when constructing an investment portfolio, as it can influence diversification, risk, and returns. By considering market capitalization when investing in stocks, investors can gauge a company based on its perceived value and make more informed decisions about the future performance of the stock of a company.
For example, large-cap companies with higher market capitalizations tend to be more stable and have greater growth potential, making them attractive investments for overweight stocks.
Analyzing Past Price Performance
Another essential aspect of investing in stocks is analyzing past price performance. By examining historical data of a stock’s price movements, investors can detect trends, patterns, and other elements that could be utilized to anticipate future price movements. This is an element of technical analysis, which uses past performance to forecast future market behavior.
Predicting Future Performance
Through analyzing past price performance, investors can gain insight into potential trends and patterns that may help them anticipate future performance. However, it is crucial to remember that past performance is not necessarily indicative of future performance, and the data used may be incomplete or inaccurate.
As such, investors should consider past performance as one of the many factors when making investment decisions. Other factors to consider might include economic indicators and analyst ratings when forecasting future performance.
Diversifying with Overweight Stocks

In the world of investing, diversification is a powerful strategy to manage risk and potentially increase returns. One way to diversify is by incorporating overweight stocks into your portfolio. These stocks have been rated higher than average by analysts, providing a higher potential for returns.
Overweight stocks, such as those found in the retail sector (e.g., Amazon, Walmart, and Target), can provide investors with higher returns than average and help diversify their portfolios, thereby reducing the overall risk of their investments.
Large-cap stocks, such as Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon, as well as mid-cap stocks, such as Tesla and Uber, are examples of overweight stocks in a diversified portfolio. By incorporating these stocks into their portfolios, investors can potentially increase returns while also diversifying their investments and minimizing risk.
The Retail Sector: A Case Study
To better understand how analyst ratings can influence stock prices, let’s take a closer look at the retail sector as a case study. The retail sector is composed of businesses that provide goods and services to customers, including physical stores and online retailers. It is a significant component of the economy and encompasses a range of retailers, including department stores, supermarkets, and specialty stores.
Factors Influencing Analyst Ratings
When assessing analyst ratings in the retail sector, factors such as projected industry growth, the quality of the top management team, the experience of the analyst, earnings quality, audit quality, IFRS adoption, annual report, volatility, indebtedness, and profitability are taken into account. These factors can play a significant role in shaping an analyst’s opinion of a stock and, consequently, its rating.
Some examples of retail sector stocks include Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN), Costco Wholesale (COST), Abercrombie & Fitch Co. (ANF), American Eagle Outfitters Inc. (AEO), and Bath & Body Works (BBWI).
Evaluating Analyst Ratings
As an investor, it’s essential to evaluate analyst ratings before making any investment decisions. While these ratings can offer valuable insights into the potential performance of a stock, they should not be taken at face value without further investigation and analysis.
Reliability of Analyst Ratings
The reliability of analyst ratings can vary depending on the analyst’s track record, the size of the firm they are affiliated with, and the accuracy of their previous predictions. Given that analyst ratings may be impacted by factors such as conflicts of interest or external pressure, it is essential to approach them with a critical perspective to ensure that the ratings are reliable and result in positive returns for investors.
Interpreting Overweight Ratings
When interpreting an overweight rating, investors should take into account the context of the rating. For instance, an overweight rating could signify that the analyst perceives the stock to be undervalued and with potential for growth, whereas an underweight rating could indicate that the analyst perceives the stock to be overvalued and with limited potential for growth.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the concept of overweight stocks and the factors that influence analyst ratings can be a valuable asset for any investor. By analyzing past price performance, considering market capitalization, and diversifying with overweight stocks, investors can make more informed decisions and potentially achieve higher returns. However, it is crucial to remember that analyst ratings should not be taken at face value, and investors must conduct their own research and analysis before making any investment decisions. With the right knowledge and tools, investors can navigate the world of investing with confidence and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is an overweight stock good?
Overall, an overweight stock rating indicates that analysts expect the stock to have above-average performance compared to its industry. Therefore, it could be a good investment.
Analysts look at factors such as positive news, strong earnings reports, and raised guidance when making the decision to recommend a stock as overweight.
Does overweight mean buy or sell?
Overall, an overweight rating means that analysts believe the stock is worth buying and could outperform other stocks in its sector or the broader market.
It is important to note that this is a buy recommendation, so investors should use their own research and analysis to make informed decisions about their investments.
Does overweight mean sell?
The advice to investors is that an “overweight” rating means that the analyst believes the stock is worth buying and has good prospects for performance.
Consequently, it does not mean “sell.”
Is overweight bullish or bearish?
Overall, an overweight stock rating is a bullish signal and suggests that analysts expect the stock to outperform. This could be a good opportunity to invest in stocks before they go up further.




