The world of Social Security Disability can be complex and confusing. But did you know there’s a rule designed to support those receiving disability benefits as they attempt to return to work? The Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule is a powerful tool that offers valuable assistance during this challenging transition. This blog post will delve into the intricacies of the 5-Year Rule, its benefits, and how it can make a difference in the lives of those navigating the Social Security Disability system.
Short Summary
The Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule enables individuals with a disability to bypass the waiting period for receiving benefits.
The Trial Work Period and Extended Period of Eligibility provide SSDI recipients with opportunities to explore their options in the workforce while continuing full or sustained benefits, respectively.
Expedited Reinstatement allows for regaining benefits within five years if income drops below a substantial gainful activity level.
Understanding the Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule

The Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule aims to enable individuals who previously received disability benefits and subsequently experienced a physical or mental disability that rendered them unable to work again within five years to bypass the obligatory waiting period for benefits. This rule applies to those who previously received benefits through Supplemental Security Income (SSI) or Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI).
The 5-Year Rule allows SSDI recipients to try returning to work without forfeiting benefits through the Trial Work Period, Extended Period of Eligibility, and Expedited Reinstatement. This rule benefits those who are not yet at their full retirement age and cannot work due to a disability.
The Trial Work Period and Its Significance
The Trial Work Period (TWP) is a provision that allows SSDI recipients to work for nine months within five years while still receiving full benefits, thus encouraging a return to the workforce. This is possible because they have already paid Social Security taxes during their previous employment. The TWP program is designed to motivate disabled workers to explore the possibility of working if they feel capable without risking their Social Security benefits.
In 2023, any month you earn a minimum of $1,050 is considered a trial work month for those with physical or mental impairments that qualify for SSDI benefits. The trial work months are valid for five years. Each person can use up to nine months within this time frame.
Extended Period of Eligibility: Continuing Benefits Beyond the Trial Work Period
The Extended Period of Eligibility (EPE) offers 36 months of sustained benefits if the recipient’s earnings remain below the SSDI income limit following the Trial Work Period. To qualify for the EPE, the recipient’s earnings must remain below the SSDI income limit after the Trial Work Period.
This program provides additional support for those attempting to return to work, allowing them to continue receiving benefits during the transition period. By offering a safety net, the EPE encourages SSDI recipients to explore their options and regain independence in the workforce.
Expedited Reinstatement: Regaining Benefits Within 5 Years
Expedited Reinstatement is a post-termination work incentive that facilitates up to 6 months of provisional cash benefits while the application is being processed. It expedites the resumption of disability benefits for individuals who return to work before a medical relapse.
The EXR allows SSDI recipients to regain benefits within five years should their income drop below the substantial gainful activity level. This ensures that they quickly regain their benefits without repeating the entire application process, saving time and money and facilitating the process of getting back on track.
The Importance of Work Credits in Social Security Disability

Work credits are crucial in determining eligibility for SSDI benefits, with individuals accumulating up to four credits annually based on their income and contributions to the Social Security system. These credits are earned through contributions to the Social Security fund and change annually.
Understanding the importance of work credits and how they impact eligibility for SSDI benefits is essential. In the following sections, we will look into earning work credits and the options available for those who may not have sufficient credits for SSDI eligibility.
Earning Work Credits: The Key to SSDI Eligibility
Earning work credits is vital for SSDI eligibility, with most applicants requiring a minimum of 20 credits within the last 10 years. Labor credits are accumulated based on annual wages gained through employment and payment of social security taxes. Other sources of income like dividends, annuities, interest, pensions, etc. are not included in it.
The more work credits an individual accumulates, the greater their eligibility for SSDI benefits. Understanding the process of earning work credits and meeting the minimum requirements is essential for successfully applying for disability benefits.
Related Article: More Interest Rate Hikes?
Insufficient Work Credits: Alternatives and Options
If an applicant lacks sufficient work credits for SSDI, they may qualify for Supplemental Security Income (SSI), which has no work history requirement but has specific income and resource limitations. To be eligible for SSI benefits, the applicant must fulfill the income and resource limitations established by the SSA and not receive any other cash benefits or payments.
Navigating the SSI application process can be challenging due to the complexity of regulations and technicalities. However, it remains a viable alternative for those not meeting the work credit requirements for SSDI benefits.
Navigating the Social Security Disability Application Process
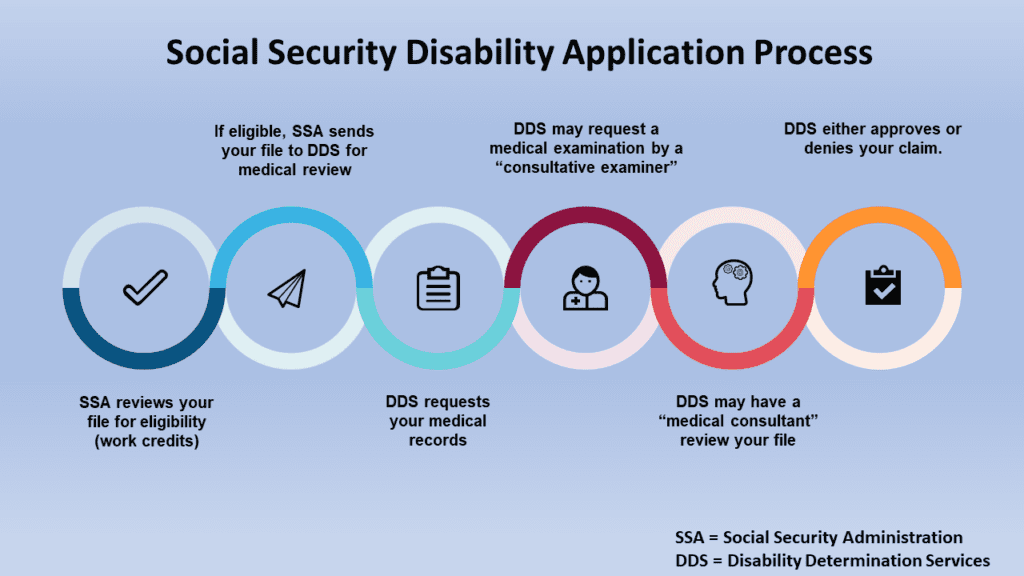
The SSDI application process involves several steps, including submitting an application, providing medical documentation, and potentially attending a disability hearing. This process can be daunting for many individuals, especially when dealing with the complexities of the Social Security system.
In the following sections, we will guide on:
How to apply for SSDI benefits
The role of medical documentation in the application process
The potential benefits of hiring an attorney to assist with your case.
How to Apply for SSDI Benefits
Applying for SSDI benefits as soon as possible is crucial, as there is the potential for back-paid benefits up to 12 months before the application date. An application for the Social Security Disability benefits can be submitted via online, by phone, or in person at a local Social Security office. Once approved, you will begin receiving disability benefits according to your eligibility.
It’s important to gather all necessary documentation and file your application promptly to maximize your chances of receiving benefits. Delaying the application process may result in lost benefits or prolonged wait times for a decision.
Medical Documentation and Its Role in the Application Process
Medical documentation plays a vital role in proving the severity and duration of a disability, including mental impairment. The Social Security Administration necessitates objective medical evidence from an acceptable medical source to ascertain that a claimant has a medically determinable impairment. One crucial form is the Residual Functional Capacity (RFC) form, which outlines the limitations an individual may experience due to their condition.
Ensuring that your medical documentation is thorough and up-to-date is essential for a successful SSDI application. This information will be reviewed by Disability Determination Services, who will decide based on the medical records and assessments provided.
The Role of an Attorney in the Social Security Disability Process

Hiring an attorney can greatly enhance the chances of a successful SSDI application. An attorney can:
Help navigate the complex process
Provide legal counsel
Represent the applicant during hearings
Offer guidance on eligibility requirements and medical evidence
Possess a comprehensive understanding of the Social Security process.
In the following sections, we will discuss why you should consider hiring an attorney for your SSDI application and how to find the right attorney for your case.
Why You Should Consider Hiring an Attorney
Considering an attorney for SSDI applications is advisable, as they can provide useful guidance and support throughout the process. The cost of hiring an attorney for Social Security Disability is limited by law, with the maximum amount set at $6,000 or 25% of the SSDI backpay.
An attorney’s skill can be invaluable in navigating the complexities of the Social Security Disability system, enhancing your chances of success and reducing stress during this difficult time.
Finding the Right Attorney for Your Case
Finding the right attorney for your case involves researching their experience, success rate, and communication style to ensure they fit your needs well. Gathering recommendations from individuals who have experienced a similar process and checking online client reviews and testimonials can aid your search.
When consulting with an attorney for your Social Security Disability case, it is important to inquire about their experience, success rate, and communication style. Choosing the correct lawyer can make or break your SSDI application process and help you reach the best possible result.
Key Factors to Remember About the Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule

In summary, the Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule is designed to support SSDI recipients returning to work, providing a safety net through various programs and benefits such as the Trial Work Period, Extended Period of Eligibility, and Expedited Reinstatement.
Understanding this rule and its benefits can help individuals navigate the complex world of Social Security Disability and make informed decisions about their future.
Summary
Throughout this blog post, we have searched the intricacies of the Social Security Disability 5-Year Rule, the importance of work credits, the application process, and the role of an attorney in SSDI cases. By understanding these key factors, individuals can better navigate the Social Security Disability system and make informed decisions about their benefits and future. Remember, knowledge is power – and in Social Security Disability, it can make all the difference in achieving a successful outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered to be a permanent disability?
A permanent disability is an impairment caused by a health condition, injury or illness that affects the ability to earn a living and persists even after a doctor has determined that the individual’s condition won’t improve. It often includes physical injuries, like spinal cord or brain injuries, and illnesses such as cancer, multiple sclerosis and chronic heart disease.
At what age does Social Security disability stop reviewing?
Social Security disability reviews end at full retirement age, currently 66 years old when your eligibility for continued benefits is evaluated and any medical condition or income changes are taken into account.
At this point, the Social Security Administration will review your case to determine if you are still eligible for benefits. They will consider any medical condition or income changes since your last review. If you are still eligible, your benefits will continue. If not, then your situation is different.
Is Social Security based on last 5 years or best 5 years?
Your benefit amount is determined by your greatest 35 years of earnings and the age at which you receive benefits. Social Security replaces an average of your pre-retirement income based on your career earnings.
Additional earnings may increase your payment.
What happens to my disability when I turn 65?
Your Social Security Disability benefits will end after you reach 65, and your retirement benefits will begin.
How apply for social security disability?
Individuals can go for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits online, by calling 1-800-772-1213 (TTY 1-800-325-0778) between 8 a.m. – 7 p.m. Monday to Friday, or by visiting their local Social Security office.
The process is simple and straightforward. All applicants must do is provide the necessary information and documents to the Social Security Administration. This involves proof of identity, proof of income, and medical records. Once the application is submitted, the Social Security Administration will review the information and decide whether the applicant is eligible for SSDI benefits.




