In the dynamic world of trading, understanding market inefficiencies and imbalances is crucial. This article explores the causes of fair value gaps, including market inefficiencies, economic indicators, interest rate differentials, and large orders by institutional players to name a few. It also outlines strategies for trading using fair value gaps, emphasizing the importance of identifying the market trend, supply and demand zones, and managing risk.
What is a Fair Value Gap?
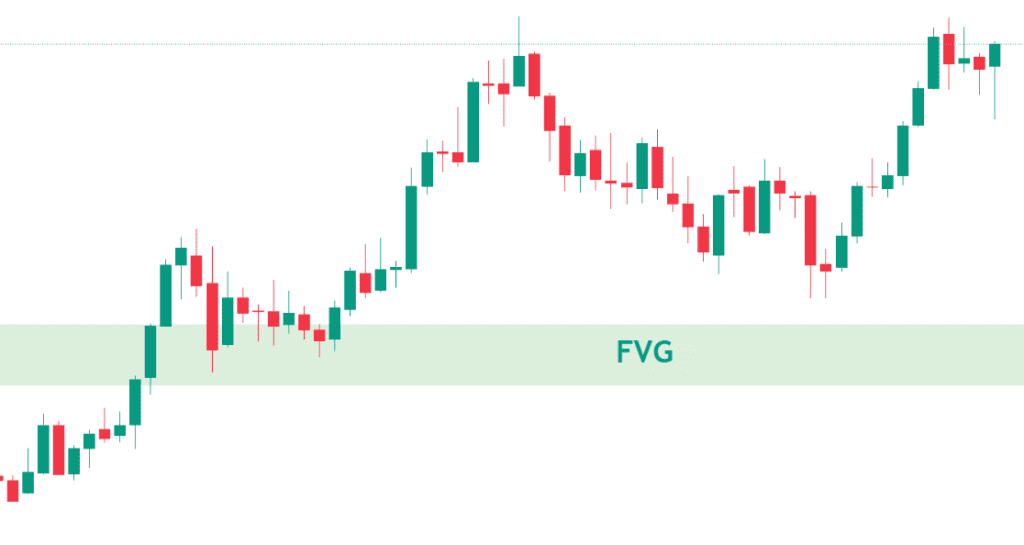
A fair value gap (FVG) is a concept used primarily by price action traders to identify market inefficiencies or imbalances. These imbalances occur when buying and selling forces are not equal, leading to significant and rapid price movements. The fair value gap is visualized on a price chart as a gap formed within a three-candle sequence. When there is a large move in either direction, a gap is formed between the first candle’s wick and the wick of the last candle. This gap is known as the Fair Value Gap.
The concept of a fair value gap is rooted in the belief that the market naturally tends to correct itself. Therefore, these gaps can become a magnet for the price before it continues in the same direction. By identifying these gaps, traders can take advantage of the temporary imbalances that arise in the market
Common Causes of A Fair Value Gap
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are caused by a variety of factors, primarily related to market inefficiencies and imbalances. Here are some common causes:
Market Inefficiencies: Fair value gaps often occur due to market inefficiencies, which are instances where the current price of an asset does not reflect its intrinsic value. These inefficiencies can arise due to a lack of information, irrational behavior by market participants, or other factors that prevent the market from functioning perfectly.
Imbalances in Buying and Selling Forces: Fair value gaps can also be caused by imbalances in buying and selling forces. When the forces exert significant pressure, it can lead to substantial and rapid price movements, creating gaps in the market.
Economic Indicators: Economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment data can significantly impact asset valuations, leading to the formation of fair value gaps. Changes in these indicators can cause the market price of an asset to deviate from its perceived fair value.
Interest Rate Differentials: Changes in interest rates can influence the fair value of assets, particularly in the forex market. If the interest rate of one country increases relative to another, it can cause the value of its currency to rise, creating a gap between the current exchange rate and its perceived fair value.
Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical events can cause sudden and significant changes in asset prices, leading to the formation of fair value gaps. These events can include political instability, changes in government policies, or international conflicts.
Large Orders by Institutional Players: Large orders placed by institutional players can cause sudden price changes without enough liquidity at a stable price, leading to the formation of fair value gaps. These gaps provide insights about where many orders were injected, creating this inefficiency in the market.
Trade Using Fair Value Gaps: The Strategy
Traders view FVGs as potential areas where price might revisit to “fill the gap.” This is because the unfilled area represents untested demand or supply.
They use this information to:
Plan entries: Enter trades close to the fair value gap, expecting a move back into the gap area.
Set stop-losses: Place stop-losses outside the fair value gap to limit potential losses if the price doesn’t fill the gap.
Identify support and resistance: Unfilled gaps can act as temporary support or resistance levels.
Here’s how to trade using FVGs:
1. Trend Direction
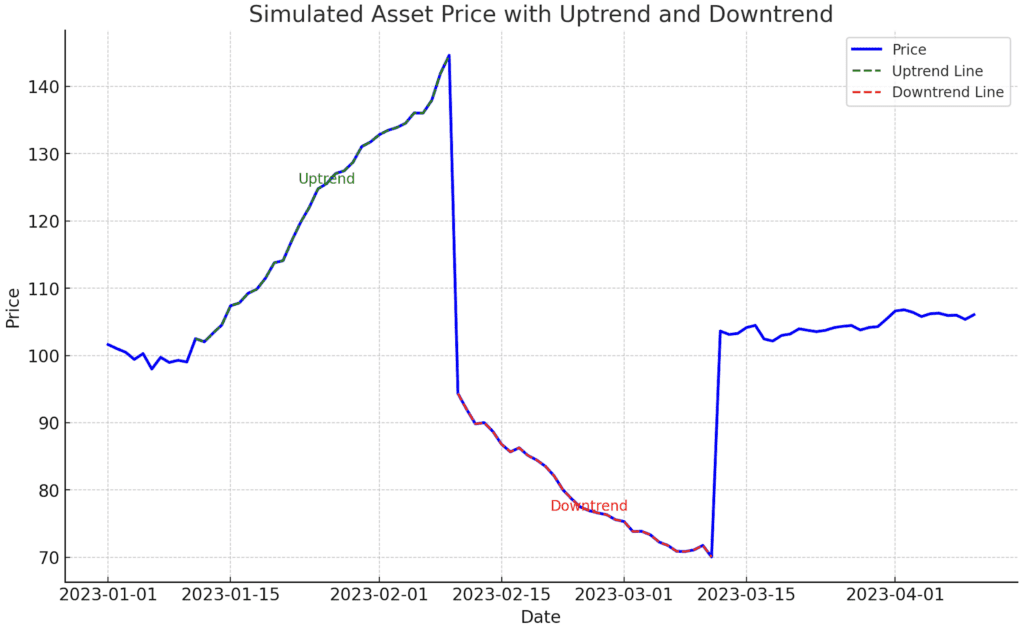
Before diving into FVGs, establish the market’s trend using higher timeframes: hourly, daily, or weekly.
Look for:
Higher highs and lows for uptrends → Buy opportunity.
Lower highs and lows for downtrends → Sell opportunity.
Tools like trend lines and channels can also help confirm the direction.
Uptrend: Focus on buying entries near demand zones (areas with strong buying) identified by FVGs.
Downtrend: Seek selling entries near supply zones (areas with heavy selling) highlighted by FVGs.
2. Find Supply & Demand Zones
These zones mark areas where significant price movements are likely to occur, aligning with the overall trend.
Demand Zones (Bullish Trend): Look for price retracements towards these zones for potential buy entries. FVGs near demand zones offer a confluence of trend and imbalance, increasing potential success.
Supply Zones (Bearish Trend): Watch for price approaches to these zones for potential sell entries. FVGs near supply zones can signal price continuation downwards, allowing you to capitalize on the bearish momentum.
3. Fair Value Gap → Entry Point
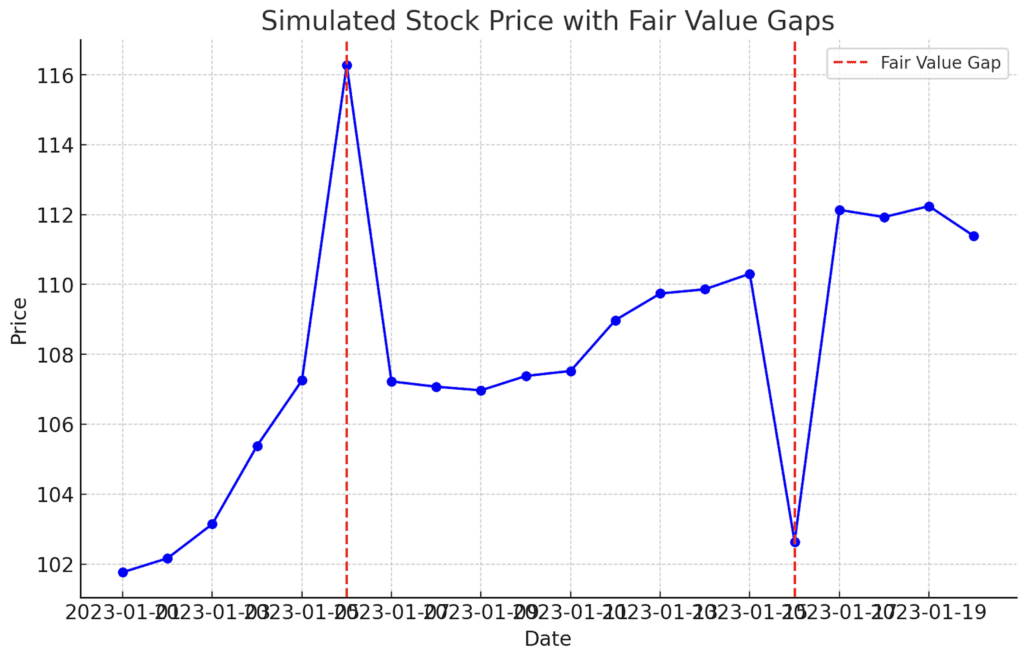
Identify the actual fair value gap formation using tools like the Fair Value Gap Indicator on TradingView. Remember, FVGs indicate potential market imbalances waiting to be corrected. When the price closes the gap, it often moves in the direction of the larger initial candle, creating your trading opportunity.
Buy Setup: If the price closes the fair value gap within a bullish trend and approaches a demand zone, consider entering a long position aiming for the next demand zone as your profit target.
Sell Setup: In a bearish trend, focus on fair value gap closures followed by price movements towards supply zones. Look for entry points near these zones and target the next supply zone for profit taking.
4. Manage your Risk & Reward
No strategy is complete without risk management. Place stop-loss orders beyond the supply/demand zones for added protection.
Stop-Loss: For buy trades from supply zones, place your stop-loss above the zone or above the first candle of the fair value gap formation. Conversely, set stop-loss orders below demand zones for sell trades.
Profit Target: Aim for realistic profit targets based on technical analysis and risk-reward ratios. You can initially target the next demand/supply zone, but adjust your take profit if you sense a stronger trend continuation.
| Trade Type | Entry Zone | Stop-Loss Placement | Profit Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buy | Demand Zone | Above Supply Zone or Fair Value Gap Candle 1 | Next Demand Zone |
| Sell | Supply Zone | Below Demand Zone | Next Supply Zone |
Pros & Cons of FVGs
1. Pros
Profit Potential: If you accurately identify and trade FVGs, the potential for profits can be significant, as you are essentially exploiting market inefficiencies.
Reduced Risk: Compared to some directional trading strategies, fair value gap trading focuses on identifying inefficiencies rather than predicting overall market direction, potentially leading to fewer losses.
Visual Confirmation: Price action patterns near FVGs can provide clear visual signals for entry and exit, simplifying trade execution for some traders.
Adaptability: The fair value gap concept can be applied to various instruments and timeframes, offering flexibility for different trading styles.
2. Cons
Misjudgment risk: The assumption that prices will “fill the gap” is not always accurate. False gaps exist, and prices might break through FVGs, leading to losses.
Market Volatility: fair value gap trading can be challenging in highly volatile markets, as rapid price movements might distort or negate gap opportunities.
Limited Opportunities: FVGs occur less frequently in efficient markets, requiring patience and potentially limiting trading opportunities.
Subjectivity: Identifying and interpreting FVGs can be subjective, requiring experience and practice to avoid misinterpretations.
Discipline Required: fair value gap trading requires strict discipline in waiting for confirmation signals and managing risk with stop-losses, as false entries can be costly.
FAQs: The Fair Value Gap Strategy
What is the difference between imbalance and Fair Value Gaps?
Think of an imbalance as the cause of a gap. It’s the underlying reason why buyers or sellers temporarily overpowered the other side.
An fair value gap is the visual result of that imbalance. It’s the actual gap left on the chart where the price skipped a price range due to the temporary imbalance.
What is the Smart Money Concept of FVG?
The Smart Money Concept of FVGs sees gaps as parts of larger market structures controlled by institutional power players, requiring deeper analysis and order flow awareness for potential trade setups.
It’s not a guaranteed trading strategy, and market dynamics can sometimes be unpredictable.
Do fair value gaps always get filled?
No, fair value gaps (FVGs) not always get filled. While the market tends to correct imbalances over time, some FVGs remain unfilled and prices move on without ever retracing back to the gap area.
Reason why they’re not always getting filled:
Other market forces: New trends, unexpected news, or changes in sentiment can drive price away from the fair value gap before it has a chance to fill.
Partial fills: Sometimes, the price retraces partially into the fair value gap but then resumes its original direction, leaving part of the gap unfilled.
Runaway gaps: Large gaps formed with sustained momentum might not retrace at all and continue the trend in the direction of the break.
Relying solely on FVGs getting filled can be risky.
Can trading with Fair Value Gaps be consistently profitable, and what are the risks?
Trading with Fair Value Gaps can be consistently profitable if traders have a sound trading strategy and effectively manage their risks. However, like any other trading strategy, Fair Value Gap trading carries risks such as market volatility.
What strategies are most effective for trading Fair Value Gaps?
The most effective strategy for trading Fair Value Gaps is to buy or sell an asset when the market price deviates significantly from its fair value. Traders can use various technical indicators to identify potential trading opportunities and set appropriate stop loss and take profit levels




