The COVID-19 crises had a massive impact on the stock market in March of 2020. There was a large decline in all indices based on fear and the unknown economic impact. Many businesses were mandated to shut down in order to curb the spread, while other businesses simply shut down due to loss of revenue. This created large layoffs which resulted in record high unemployment numbers seen below.
source: tradingeconomics.com
As people lost their income, they began to spend less and save more, which contributed to a decline in GDP. Furthermore, there were global supply chain problems which limited supply and drove up the prices of food, cars, metals, lumber, and many other resources.
In an effort to prevent a nation wide recession, the federal government and the federal reserve stepped in to support and stimulate the economy.
Actions Taken by the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve is the central banking system in the U.S. It aims to support the economy by helping with monetary policy. When the pandemic hit the U.S, there was a major risk of a recession. If companies go bankrupt, they lay off their employees, which means people don’t have disposable income so they limit their spending.
A decrease in consumer spending could result in revenue declines among other businesses which could result in additional layoffs. This virtuous cycle is self-reinforcing and can lead to a major recession. In order to avoid such a scenario, federal reserve stepped in to support the economy in 2 ways: interest rate cuts and quantitative easing (QE)
Interest rate cuts
Throughout 2020 the federal reserve announced multiple interest rate cuts in order to provide liquidity through debt. When interest rates are low, people and businesses tend to borrow more money. Therefore, many companies borrowed money to support their expenses and invest in growth. When interest rates are very low, investors who typically make a return through safe investments in corporate or government bonds, will no longer make a return. This promotes the shift of investment into higher risk/return assets like stocks.
Therefore as the federal reserve lowered interest rates, there was a big money influx of funds into the stock market where returns were much higher. The huge influx of money into the stock market increased the demand for these assets and resulted in an aggressive bull run since April 2020.
Tech and growth companies especially benefited from this run as their revenues began to increase from the shift to working from home and their valuation/revenue multiples increased. When interest rates are low, investors are willing to pay higher multiples for a given company.
Quantitative Easing (QE)
Quantitative easing involves the federal reserve directly buying assets like government bonds, corporate bonds, and even stocks, in order to increase liquidity in the market and lower inflation. QE enables the government and companies to issue more debt and gain liquidity during rough times.
When the federal reserve buys government bonds, it enables the government to increase spending on unemployment programs and other methods to support the country and the people. QE also involved large purchases of stocks by the federal reserve which contributed to the large increases in the stock market over the past couple of years.
This is often referred to as the federal reserve “expanding their balance sheet”. The below graph visualizes the increase in the Fed’s balance sheet over the past few years.
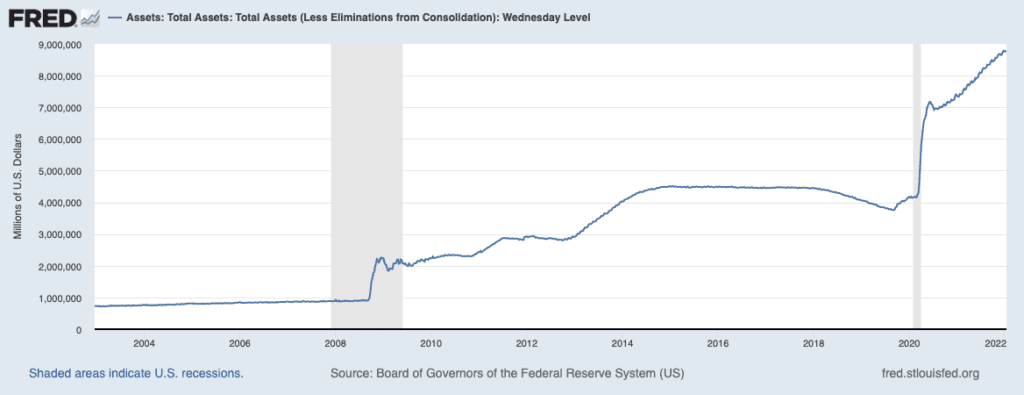
To support the purchase of assets, the federal reserve “printed” trillions of dollars which could have consequences like an increase in inflation and devaluation of the U.S dollar. Quantitative easing also has the risk of creating asset bubbles where assets like stocks and real estate can become overvalued if their prices have increased without a meaningful change in the fundamentals.
Actions Taken by the Federal Government
The monetary policy issues by the federal reserve was largely to support the U.S banking system, companies, and the stock market. The U.S federal government issues fiscal policy in parallel to provide economic relief for individuals, states, and municipalities. This fiscal policy took the form of multiple stimulus and relief packages that totaled trillions of dollars. The main objectives of this stimulus was to:
- Provide financial aid for individuals and households during rough times
- Support research and distribution of vaccines and test kits
- Provide additional funding for schools, hospitals, and other public institutions
- Support small businesses through loans and payroll credits
In order to spend trillions of dollars on this fiscal policy, the federal reserve “printed” even more money over the past couple of years. As mentioned earlier, printing money increases the supply of money in the system which can lead to inflation and a weaker U.S dollar. Rising inflation can lead to the increase of interest rates which will have a negative impact on the stock market.
Recent News of QE and Inflation
On January 5th, the meeting notes from a federal reserve meeting held in December were released to the public. Conversations from this meeting indicated that the federal reserve is thinking about increasing interest rates sooner than they had initially planned. This resulted in the decline of many stocks and indices, with the SPY declining 1.92% and IWM declining 3.39%.
Increased interest rates make it less compelling for investors to put their money in higher risk assets like the stock market. This is because investors can get a decent return on very low risk assets like corporate and government bonds during a high interest environment. The talks around increasing interest rates could result in large outflows from the stock market which further reduces demand and decreases valuation to revenue multiples for many stocks. This is called multiple contraction.
Furthermore, some participants in that meeting indicated that it could be an appropriate time to start reducing the Fed’s balance sheet. This means that the federal reserve could stop buying bonds and stocks very soon (end QE). In fact, when the Fed reduces it’s balance sheet, this involves the selling of the bonds and assets they purchased which could result in a further decline in the stock market.
Conclusion
Recent events around quantitative easing and inflation are still ongoing. The federal reserve is trying to balance supporting the economy in the short term while considering the long term economical impact of current efforts. To summarize, in this article we discussed:
- The actions the federal reserve and the federal government took in response to COVID-19
- The positive performance in the stock market as a result of low interest rates and increased liquidity
- The recent discussions at the federal reserve to increase interest rates and stop QE which is resulting in multiple contraction and a decline in the stock market




