When it comes to investing in the stock market, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have become increasingly popular due to their low costs, diversification benefits, and ease of trading. Two of the most well-known and widely traded ETFs are the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) and the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO). Both funds track the performance of the S&P 500 index, which comprises 500 of the largest U.S. companies.
While SPY and VOO share many similarities, there are some key differences that investors should consider when deciding between the two. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the nuances of SPY vs VOO to help you determine which ETF is the better choice for your investment portfolio
Key Takeaways
- Both SPY and VOO track the S&P 500 index and offer broad exposure to large-cap U.S. stocks.
- VOO has a lower expense ratio of 0.03% compared to SPY’s 0.09%, which can lead to slightly higher returns for VOO over the long term.
- SPY has higher trading volume and liquidity, making it potentially more suitable for frequent traders.
- For long-term, buy-and-hold investors, VOO is generally the better choice due to its lower expense ratio.
- Investors should consider their individual investment goals, trading frequency, and broker offerings when deciding between SPY and VOO
Related Article: Vanguard Statistics.
Comparison: SPY vs VOO
Historically, SPY and VOO have delivered very similar performance, as they both track the same underlying index. However, there may be slight differences in returns due to the difference in expense ratios.
| Feature | SPY (SPDR S&P 500) | VOO (Vanguard S&P 500) |
|---|---|---|
| Index Tracked | S&P 500 | S&P 500 |
| Expense Ratio | 0.09% | 0.03% |
| Average Daily Volume | Higher | Lower |
| Issuer | State Street Global Advisors | Vanguard |
| Returns (1 Year) | 21.88% | 21.42% |
| Returns (10 Year Annualized) | 12.23% | 12.29% |
While the difference in annualized returns may seem small, it can compound significantly over time. For example, on a $10,000 investment over 20 years, assuming a 7% annual return, the difference in fees between SPY and VOO can result in a performance gap of over $1,500. Let’s break down the most important parts.
1. Expense Ratio
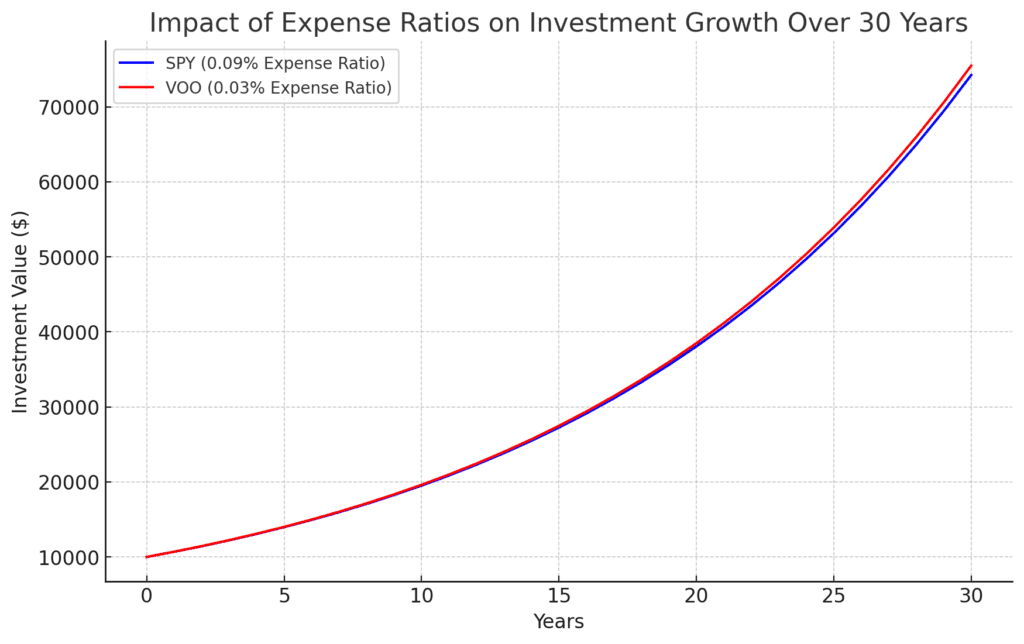
One of the most significant differences between SPY and VOO is their expense ratios:
- SPY Expense Ratio: 0.09%
- VOO Expense Ratio: 0.03%
The expense ratio represents the annual fee charged by the ETF, which is deducted from the fund’s assets. A lower expense ratio means that investors get to keep more of their investment returns. While the 0.06% difference may seem small, it can add up over time, making VOO the more cost-effective choice for long-term investors
A seemingly small difference of 0.06% in expense ratio can compound significantly over time.
For example: On a $10,000 investment, a 0.09% expense ratio translates to $9 annually, while a 0.03% expense ratio equates to only $3. Over 20 years, assuming a 7% annual return, this difference in fees can result in a performance gap of over $1,500.
Expense ratios eat into your investment returns. Lower expense ratios allow you to keep more of your profits.
VOO has a significantly lower expense ratio, meaning it charges less in fees each year. This can lead to slightly higher returns over the long term.
2. Performance
- SPY:
- YTD Return (as of April 23, 2024): 5.46%
- 10-Year Annualized Return: 12.40%
- VOO:
- YTD Return (as of April 23, 2024): 5.43%
- 10-Year Annualized Return: 12.47%
Historically, both funds have delivered very similar performance. There may be slight differences year-to-year, but overall returns are nearly identical.
3. Holdings
- SPY: Tracks the S&P 500 Index.
- VOO: Tracks the S&P 500 Index.
Both SPY and VOO offer identical holdings, providing complete exposure to the S&P 500.
4. Liquidity and Trading Volume
Another factor to consider when choosing between SPY and VOO is liquidity and trading volume:
- SPY has higher average daily trading volume, resulting in tighter bid-ask spreads.
- VOO has lower trading volume and slightly wider spreads.
For frequent traders, the higher liquidity of SPY may be advantageous, as it can potentially lead to lower trading costs. However, for long-term investors, the difference in liquidity is less important
5. Other factors to consider
- Tax Efficiency:
- SPY: Generally tax-efficient.
- VOO: May have a slight edge due to internal optimization techniques.
- Dividend Reinvestment (DRIP):
- SPY: DRIP options often free with some brokers.
- VOO: DRIP may incur fees with some brokers.
Which ETF Should You Choose?
Ultimately, the choice between SPY and VOO depends on your individual investment goals and preferences:
- For long-term, buy-and-hold investors, VOO is generally the better choice due to its lower expense ratio.
- For frequent traders, SPY may be more suitable due to its higher liquidity and potentially lower trading costs.
Other SPY vs VOO considerations:
- Lower fees: Choose VOO.
- Tighter spreads: Choose SPY (if you trade frequently).
- Free DRIP: Consider which ETF your broker offers free DRIP with.
- Tax efficiency: Both are good, but VOO might have a slight advantage.
Conclusion
Our take is that:
- VOO has a lower expense ratio, making it a more cost-effective option.
- SPY may have slightly better liquidity due to its larger size.
For most investors, the lower expense ratio of VOO makes it the more attractive choice. However, if you prioritize extreme liquidity and already have a broker with commission-free trading for SPY, it might be a negligible difference.
There are also other S&P 500 ETFs with even lower expense ratios, though they may have slightly lower daily trading volume.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is “SPY”?
SPY is the ticker symbol for an ETF called the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust. SPY isn’t an abbreviation for “S&P 500” itself.
This ETF tracks the performance of the S&P 500 index, which means it holds all the same stocks as the S&P 500 in roughly the same proportions. So, by owning SPY, you’re essentially investing in a basket of the 500 largest U.S. companies.
What is “VOO”?
VOO is the ticker symbol for the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF, just like SPY is for the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust. Both VOO and SPY are ETFs that track the S&P 500 index, meaning they invest in the same 500 large-cap US companies in similar proportions.
The main difference between VOO and SPY is the expense ratio, which is the annual fee charged by the ETF.
Is it wise to invest in SPY and VOO?
No, it wouldn’t be wise to invest in both SPY and VOO because they are essentially the same investment.
- Both SPY and VOO are ETFs that track the S&P 500 index.
- This means they invest in the same 500 large-cap US companies in very similar proportions.
- Owning both wouldn’t provide any additional diversification in your portfolio.
Instead…
Choose one: If you’re set on an S&P 500 ETF, deciding between VOO or SPY comes down to a very small difference in expense ratio. VOO typically has a slight edge here.
Consider a broader market ETF: If you want broader diversification, you could look at ETFs that track a wider range of stocks, such as the entire US stock market (like VTI) or a combination of US and international stocks.




