In the world of investing, managing risk is just as important as seeking returns. One strategy that allows investors to protect their stock holdings while still participating in potential upside is the protective put. This options-based approach acts as an insurance policy, limiting downside risk in case the stock price takes a tumble. In this article, we’ll dive into the mechanics of protective puts, explore real-world examples, and weigh the pros and cons to help you determine if this strategy aligns with your investment goals.
What Is a Protective Put?
A protective put is an options strategy used to hedge against potential losses in a stock that you already own. It’s like an insurance policy for your stock holdings. Here’s how it works:
- You buy a put option contract with a strike price at or near the current price of the stock you own.
- If the stock price goes down, the put option increases in value, offsetting some of your losses in the stock.
- If the stock price goes up, you still benefit from the gains in the stock, but your profits will be reduced by the cost of the put option (called the premium).
Let’s go in-depth on how it works.
How a Protective Put works
1. Buying the Put
- You buy a put option contract alongside the stock you already own (or want to protect).
- This put option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell your stock at a certain price (called the strike price) by a certain time (expiration date).
2. Protection Against Downside
- If the stock price goes down, you can exercise the put option and sell your stock at the strike price, which will be higher than the lower market price. This limits your loss.
- The put option acts like a floor price for your stock.
3. Trade-Offs
- This protection comes at a cost. You have to pay a premium to buy the put option.
- If the stock price goes up, you make money on your stock holding, but the put option expires worthless, and you lose the premium you paid.
Real-Life Example: Protective Put
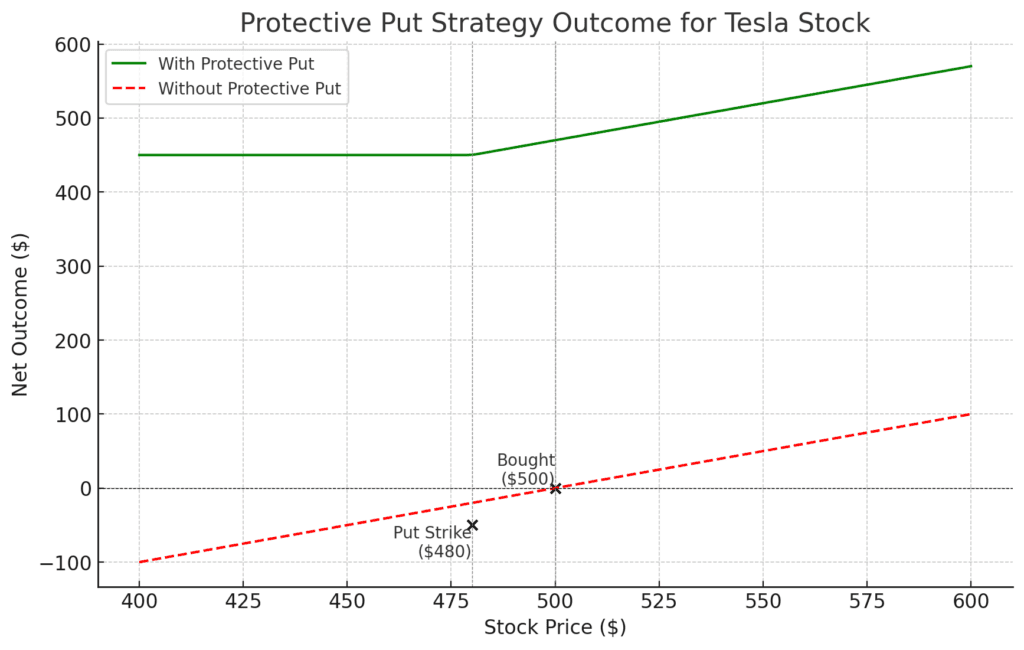
Let’s talk about Tesla (TSLA). Imagine it’s early 2020, and you own shares of Tesla that you bought at $500 each.
The stock has been doing well, but you’re worried about potential volatility in the market, maybe due to global economic uncertainties.
- So, you decide to buy a protective put option for your Tesla shares to hedge against a potential drop in stock price.
- You buy a put option with a strike price of $480, expiring in three months, for a premium of, say, $30 per share.
- This means you’re paying $30 for the right, but not the obligation, to sell your Tesla shares at $480 each, no matter what the market price is, until the expiration date.
Fast forward two months: Let’s say the market did take a downturn, and Tesla’s stock price dropped to $450.
- Because you hold the put option, you can still sell your shares at $480, protecting you from a more significant loss.
- Your net selling price would be $480 minus the $30 premium you paid for the put, which is $450, exactly the current market price.
- So, the protective put worked as insurance, preventing further losses beyond the premium you paid.
In this scenario: The protective put option served as a safety net, allowing you to limit your downside risk while still participating in any upside potential had the stock continued to rise.
Are Protective Puts Good?
Pros and Cons are going to help answer the question way easier.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Downside Protection: Limits potential losses. | Cost: Premiums paid reduce overall returns. |
| Upside Potential: Benefits from stock price increases remain. | Time-Sensitive: Protection is temporary and may need renewal. |
| Peace of Mind: Reduces stress during market volatility. | Opportunity Cost: Funds used for premiums could be invested elsewhere. |
| Flexibility: Strike price and expiration can be tailored to needs. | Complexity: Requires understanding of options and market strategies. |
Pros
- Downside Protection: The main advantage is that it offers a safety net against a decline in the stock price, effectively setting a floor for your potential losses.
- Upside Potential: You still get to benefit from any upside potential if the stock price rises, as the put only serves as insurance and doesn’t cap your gains.
- Peace of Mind: Having a protective put can provide peace of mind during volatile market conditions, knowing your investment has a layer of protection.
- Flexibility: You can select the strike price and expiration date that best fit your risk tolerance and market outlook.
Cons
- Cost: The premium paid for the put option is a direct cost, which can reduce overall returns, especially if the stock remains stable or increases in value.
- Time-Sensitive: Protective puts have an expiration date, meaning the protection is only temporary. You may need to purchase new puts periodically, incurring more costs.
- Opportunity Cost: The money spent on put premiums could potentially be used for other investment opportunities.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing protective puts require a certain level of market knowledge and sophistication, making it less suitable for novice investors.
Conclusion
Protective puts offer investors a way to hedge their stock positions against potential losses while still maintaining exposure to upside potential. By purchasing put options alongside their stock holdings, investors can effectively set a floor for their losses, providing peace of mind during market volatility. However, this protection comes at a cost, as the premiums paid for the put options can eat into overall returns.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a protective put work?
The put option gives the investor the right to sell their stock at the strike price by expiration. If the stock drops below the strike, the put gains value, offsetting losses in the stock. If the stock rises, the investor still benefits but the put expires worthless.
What are the benefits of protective puts?
- Limits downside risk while maintaining upside potential
- Provides peace of mind during market volatility
- Allows customization of protection level via strike price selection
- Useful for temporary hedging around events or time periods
What are the drawbacks of protective puts?
- Puts have an upfront cost (the premium) which eats into returns
- Time decay erodes put value if the stock doesn’t move as expected
- Volatility changes impact put pricing and effectiveness
- Not meant for constant, long-term use due to recurring costs
What factors impact the pricing of protective puts?
The main factors are the put’s strike price relative to stock price, time to expiration, implied volatility, and interest rates. Puts closer to the money, with more time, and in higher volatility environments are more expensive.




