IKEA, a name synonymous with affordable and stylish furniture, is a fascinating study of successful global branding. Known for its flat-pack furniture and Swedish meatballs, the company’s impact extends beyond the retail floor. With a unique business model, complex ownership structure, and ambitious sustainability goals, there’s much more to IKEA than meets the eye.
IKEA currently holds the position of the world’s leading furniture retailer.
As of 2021, the company operates in 50 countries, boasting a vast network of 422 stores.
The annual revenue of IKEA in the same year amounted to a remarkable $44.6 billion.
As we delve into the intricacies of the brand, we’ll uncover IKEA’s stock and explore viable alternatives for keen investors.
Short Summary
IKEA is privately owned and off the stock market, controlled by Interogo Foundation.
IKEA’s success can be attributed to its commitment to simplicity in design, cost-efficiency & self-assembly. Targeting middle-class consumers.
Alternatives for investing in home furnishings include Lowe’s Companies Inc., TJX Companies Inc., and Wayfair Inc., plus environmental & social initiatives from IKEA itself.
IKEA’s Ownership Structure
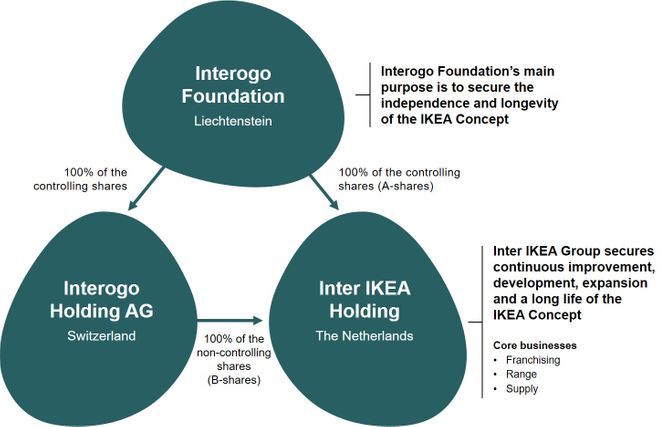
Peeling back the layers of IKEA’s corporate structure reveals a complex web of entities. At the core of it all is the Interogo Foundation and an intricate franchising system. Together, they hold the reins of IKEA’s global operations, ensuring that the unique essence of the IKEA brand remains intact across all markets. But IKEA’s choice to remain privately owned has more implications than mere brand preservation. It’s a strategic move that keeps the company off the stock market, shielding it from outside interference.
Indeed, IKEA’s decision to remain a private entity is largely due to the Interogo Foundation’s commanding influence. As the controlling shareholder in Inter IKEA Holding B.V. and Interogo Holding AG, the Foundation effectively keeps IKEA off the stock exchange. This allows the company to abstain from the transparency that public trading necessitates, ensuring IKEA’s operations remain under wraps – a crucial element in maintaining the distinct IKEA brand.
Interogo Foundation
Established in 1989 in Liechtenstein, the Interogo Foundation plays a pivotal role in IKEA’s private status. Its primary objective? Ensuring the autonomy and sustainability of the IKEA Concept. As the ultimate and controlling shareholder in Inter IKEA Holding B.V., as well as the sole shareholder of Interogo Holding AG, the Foundation ensures IKEA remains privately held.
This strategic ownership structure ensures that IKEA continues to operate without the pressures of stock market fluctuations, allowing it to focus on its unique business model and customer-centric approach.
Franchising System
Alongside the Interogo Foundation, IKEA’s franchising system plays a key role in the company’s ownership structure. It’s the engine that drives IKEA’s global operations, ensuring the IKEA experience is uniform across all markets. Crucially, the franchising system allows IKEA to remain off the stock exchange, keeping IKEA stock prices off the radar of potential investors.
In other words, while customers worldwide can assemble their own Billy bookcases, they cannot buy a piece from the company that created them. A unique strategy, indeed, but one that has undoubtedly contributed to IKEA’s distinct business model and international success.
Understanding IKEA’s Business Model

IKEA’s business model is as unique as its product designs. At its core, it revolves around simplicity in design, cost-efficiency, self-assembly, and a keen focus on middle-class consumers. This simple yet powerful approach has catapulted IKEA to the forefront of the furniture industry, making it a household name across continents.
IKEA’s journey began in 1943, under the helm of founder Ingvar Kamprad. What started as a small local business in Sweden has today transformed into a global brand, with 464 stores spread across the world by 2021. Key to this success has been IKEA’s commitment to simplicity, both in design and customer experience. By offering self-assembled, modern, and low-cost furniture, IKEA has successfully catered to a diverse range of customers looking for affordable yet stylish options, both in-store and online.
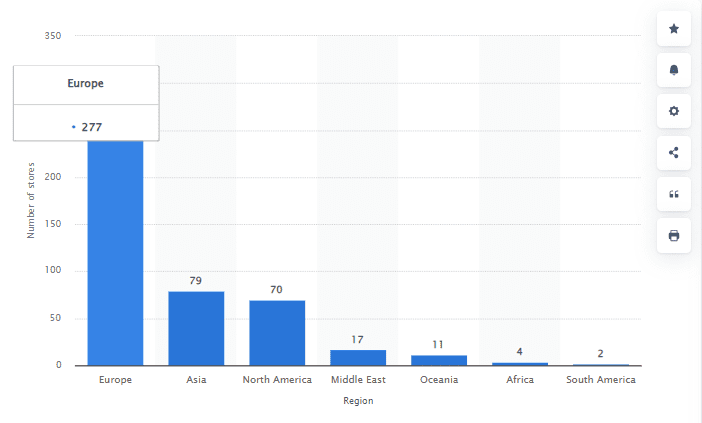
IKEA’s expansion over the years has been strategic and calculated. After launching in Sweden, it wasn’t until the 1980s that IKEA set foot in the United States and the United Kingdom. A few decades later, in 2010, IKEA ventured into Latin America, marking another significant milestone in its global expansion. Despite the COVID-19 pandemic challenges, IKEA has continued to forge ahead with its growth strategy, opening new stores and expanding its reach.
Simplicity in Design
IKEA’s simplicity in design is more than just a design philosophy; it’s a key business strategy. By designing products that are simple yet functional, IKEA has remained true to its Scandinavian design aesthetic while appealing to a diverse range of customers around the world.
This design strategy, coupled with the self-assembling concept, has made IKEA stand out in the crowded furniture market, earning it a loyal customer base and making its furniture products instantly recognizable.
Low Cost & Self-Assembly
IKEA’s low-cost and self-assembling approach is a masterstroke in cost efficiency. By implementing cost-saving measures throughout its supply chain, such as bulk purchasing of raw materials and efficient production processes, IKEA has managed to keep its prices low without compromising on quality.
Moreover, the self-assembling concept allows IKEA to save on construction costs, one of the most costly aspects of furniture production. As a result, IKEA can offer high-quality products at affordable prices, making it a go-to choice for budget-conscious consumers.
Targeting Middle-Class Consumers
At its core, IKEA is a brand for the people. It specifically targets middle-class consumers, offering a broad selection of products to cater to various financial and aesthetic preferences. From college students looking to furnish their first apartments to families seeking to revamp their homes, IKEA’s product range appeals to a wide demographic.
This strategy has not only broadened IKEA’s customer base but also made it a preferred choice for a significant portion of the global furniture market.
Financial Performance and Net Sales
A peek into IKEA’s financial performance reveals a picture of robust growth and consistent revenues. In the fiscal year ending 2022, the Inter IKEA Group reported total revenues of €44.6 billion, an increase of 6.5% in retail sales from the previous year. This growth trajectory reflects IKEA’s successful business model and its ability to navigate the complexities of the global furniture market.
Related Article: Understanding Unrealized Gains
Annual Net Income
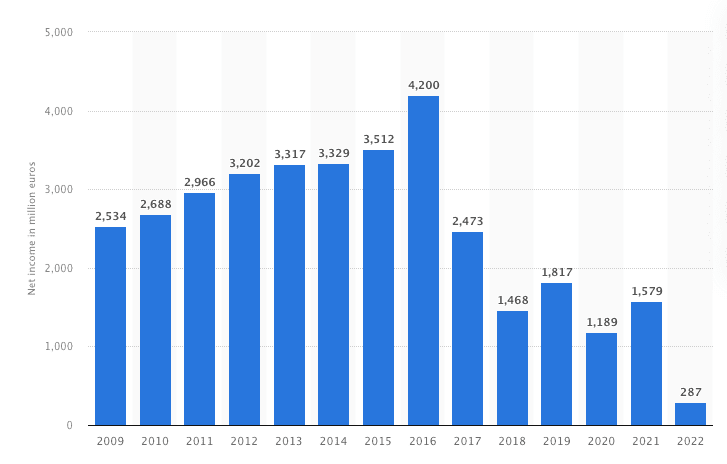
Source: Statista
While IKEA’s revenues have been on the rise, its annual net income tells a different story. The company’s net income for 2022 was a whopping €287 Million ($322 Million), marking a significant decrease from previous years. This decline in annual net income is a noteworthy aspect of IKEA’s financial performance and may have played a role in its decision to remain private.
As a private company, IKEA can navigate its financial challenges without the scrutiny and volatility of the stock market, unlike a publicly held company.
Recent Financial Performance
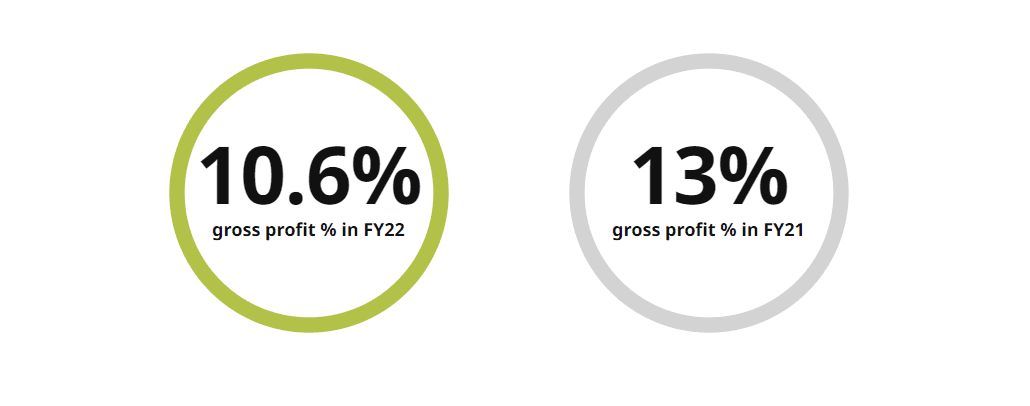
Inter IKEA Group: Source
IKEA’s recent financial performance paints a picture of a company in transformation. As part of its future growth strategy, IKEA has shifted its focus towards digital marketing and sustainability. These strategic changes have been reflected in its financial performance, with the company continuing to invest in renewable energy and aiming to achieve full sustainability by 2030.
Additionally, IKEA’s emphasis on digital marketing signals its intent to enhance its positioning and performance in key markets, particularly in the United States.
Why IKEA Isn’t Publicly Traded
Given IKEA’s global success and popularity, one might wonder why the company isn’t publicly traded. The answer lies in IKEA’s unique ownership structure and its desire for privacy. As a privately-held company, IKEA is not obligated to disclose extensive financial information, a requirement for publicly traded companies. This allows IKEA to maintain control over its operations and make strategic decisions without external pressure.
IKEA’s absence from the stock market also means that it doesn’t have a stock symbol. Prospective investors looking to buy IKEA stock will find no such option available. This lack of public trading not only adds to IKEA’s appeal but also signifies the company’s commitment to preserving its brand and operational autonomy.
No Stock Exchange Listing
IKEA’s absence from stock exchange listings is a strategic decision rooted in the company’s ownership structure. Being privately held by the Interogo Foundation, IKEA remains off the trading floor, negating the need for a stock symbol or stock price and making the possibility of an IKEA IPO unlikely.
For investors, this means they cannot buy IKEA shares directly from the stock market. Instead, they must seek alternative investment options, such as investing in private equity firms or sustainable furniture companies.
Avoiding Transparency
IKEA’s decision to remain private also allows it to avoid the transparency requirements of being a publicly traded company. As a private entity, IKEA can control the disclosure of its financials and operational strategies, thereby maintaining an air of mystery around its business operations.
This privacy not only helps IKEA protect its business strategies but also safeguards the company’s long-term growth and sustainability goals.
Alternatives to Investing in IKEA
While IKEA’s shares may not be up for grabs, investment opportunities abound in the home furnishings sector. For investors looking to tap into this market, companies like Lowe’s Companies Inc., TJX Companies Inc., and Wayfair Inc. offer viable alternatives. These companies, while not identical to IKEA, nevertheless operate in the same sector and offer potential growth opportunities.
Lowe’s Companies Inc. (NYSE: LOW)
Lowe’s Companies Inc., a home improvement company, is one such alternative. Not only is it a direct competitor to IKEA, but it also boasts expanding revenues and a healthy cash flow, making it an attractive investment option.
TJX Companies Inc. (NYSE: TJX)
Another potential investment option is TJX Companies Inc. Known for offering discounted, high-quality products, TJX is a direct competitor to IKEA. What sets TJX apart is its impressive dividend for investors, making it an attractive investment proposition.
Additionally, Investors can benefit from TJX’s 1.56% annual dividend yield.
Wayfair Inc. (NYSE: W)
For investors interested in the online retail space, Wayfair Inc. presents a compelling alternative. As an American furniture and home-goods e-commerce platform, Wayfair boasts a high number of active customers and consistent revenue growth. Its online-focused business model and significant customer base make Wayfair a strong contender in the home goods sector.
IKEA’s Environmental and Social Initiatives
Beyond its business operations, IKEA is also dedicated to making a positive impact on the environment and the society. The company’s ambitious environmental and social initiatives reflect its commitment to sustainability and its employees. From setting net-zero goals to implementing employee-focused programs, IKEA is leading the way in corporate responsibility.
IKEA has also set a goal to become climate positive by 2030.
Net-Zero Goals
As part of its sustainability efforts, IKEA has set a goal to be net zero by 2030. The company plans to achieve this by using electric trucks for deliveries and upgrading the electric vehicle charging infrastructure at its retail locations. These initiatives not only help reduce IKEA’s carbon footprint but also set a benchmark for other companies in the sector.
IKEA’s commitment to sustainability is a great example of how businesses can take advantage of sustainability.
Employee Initiatives
IKEA’s commitment to its employees is equally commendable. The company offers a variety of benefits and initiatives for its staff, from insurance and wellness programs to bonus schemes and discounted meals. Most notably, IKEA has implemented a 6% wage increase for its workers, further demonstrating its commitment to its employees.
This is a clear indication of the company’s dedication to its employees and their well-being.
Summary
To sum up, IKEA’s success story is a testament to its unique business model, complex ownership structure, and strong financial performance. While IKEA’s shares may not be available for purchase on the stock market, investors have several alternatives to consider. Above all, IKEA’s commitment to environmental and social initiatives sets a benchmark for other companies, demonstrating that financial success and corporate responsibility can indeed go hand in hand.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is IKEA a publicly traded stock?
IKEA is not publicly traded as it is privately held by the Interogo Foundation. Therefore, it has never been listed on a stock exchange and doesn’t have a stock ticker.
What company owns IKEA?
IKEA is owned by Inter IKEA Holding SA, which is further owned by the Interogo Foundation, a non-profit created to preserve the Kamprad family’s wealth and support charitable initiatives.
What is IKEA’s business model?
IKEA’s business model focuses on providing affordable, easy-to-assemble products to middle-class consumers.
Who is the CEO of IKEA
Jesper Brodin is currently the chief executive officer of IKEA.




